LSTM 和GRU的区别
Reference:https://cs224d.stanford.edu/lecture_notes/LectureNotes4.pdfEmpirical Evaluation of Gated Recurrent Neural Networks on Sequence Modelinghttps://feature.engineering/difference-between-lstm-a
先给出一些结论:
- GRU和LSTM的性能在很多任务上不分伯仲。
- GRU 参数更少因此更容易收敛,但是数据集很大的情况下,LSTM表达性能更好。
- 从结构上来说,GRU只有两个门(update和reset),LSTM有三个门(forget,input,output),GRU直接将hidden state 传给下一个单元,而LSTM则用memory cell 把hidden state 包装起来。
1. 基本结构
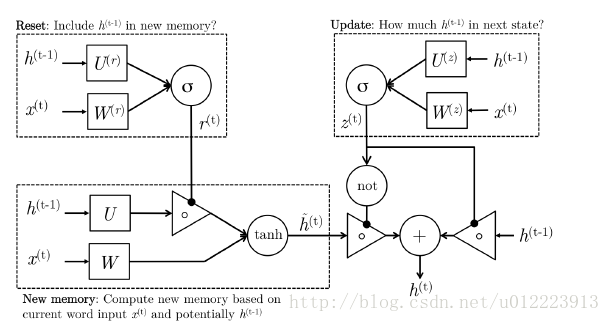
1.1 GRU
GRU的设计是为了更好的捕捉long-term dependencies。我们先来看看输入 ht−1 <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-70">h_{t-1}</script>和 x(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-71">x^{(t)}</script>, GRU怎么通过计算输出 h(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-72">h^{(t)}</script>:
-
Reset gate
r(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-73">r^{(t)}</script> 负责决定 h(t−1) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-74">h^{(t-1)}</script> 对new memory h^(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-75">\hat{h}^{(t)}</script> 的重要性有多大, 如果 r(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-76">r^{(t)}</script> 约等于0 的话, h(t−1) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-77">h^{(t-1)}</script> 就不会传递给new memory h^(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-78">\hat{h}^{(t)}</script>
-
new memory
h^(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-79">\hat{h}^{(t)}</script> 是对新的输入 x(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-80">x^{(t)}</script> 和上一时刻的hidden state h(t−1) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-81">h^{(t-1)}</script> 的总结。计算总结出的新的向量 h^(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-82">\hat{h}^{(t)}</script> 包含上文信息和新的输入 x(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-83">x^{(t)}</script>.
-
Update gate
z(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-84">z^{(t)}</script> 负责决定传递多少 ht−1 <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-85">h^{t-1}</script>给 ht <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-86">h^t</script> 。 如果 z(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-87">z^{(t)}</script> 约等于1的话, ht−1 <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-88">h^{t-1}</script> 几乎会直接复制给 ht <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-89">h^t</script> ,相反,如果 z(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-90">z^{(t)}</script> 约等于0, new memory h^(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-91">\hat{h}^{(t)}</script> 直接传递给 ht <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-92">h^t</script>.
-
Hidden state:
h(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-93">h^{(t)}</script> 由 h(t−1) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-94">h^{(t-1)}</script> 和 h^(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-95">\hat{h}^{(t)}</script> 相加得到,两者的权重由update gate z(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-96">z^{(t)}</script> 控制。
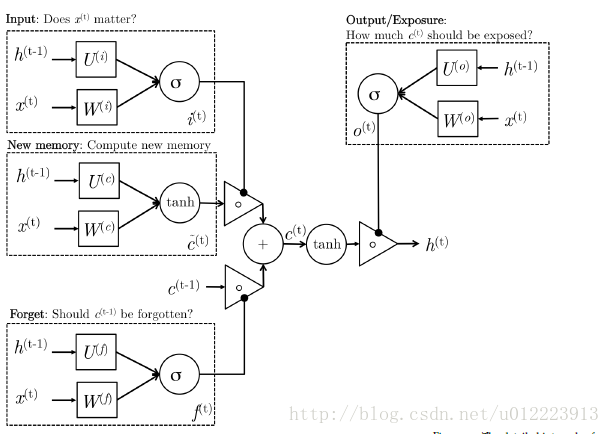
1.2 LSTM
LSTM 的设计也是为了更好的捕捉long-term dependencies,但是结构上有一些不同,更复杂一些,我们想来看看计算过程:
-
new memory cell
这一步和GRU中的new memory类似,输出的向量 c^(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-28">\hat{c}^{(t)}</script>都是对新的输入 x(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-29">x^{(t)}</script> 和上一时刻的hidden state h(t−1) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-30">h^{(t-1)}</script> 的总结。
-
Input gate
i(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-31">i^{(t)}</script>负责决定输入的 x(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-32">x^{(t)}</script> 信息是否值得保存。
-
Forget gate
f(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-33">f^{(t)}</script>负责决定past memory cell c^(t−1) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-34">\hat{c}^{(t-1 )}</script>对 c(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-35">c^{(t)}</script> 的重要性。
-
final memory cell
c(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-36">c^{(t)}</script> 由 c^(t−1) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-37">\hat{c}^{(t-1 )}</script> 和 c^(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-38">\hat{c}^{(t)}</script> 相加得到,权重分别由 Forget gate 和Input gate 决定
-
Output gate
这个门是GRU没有的。它负责决定 c(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-39">c^{(t)}</script> 中的哪些部分应该传递给hidden state h(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-40"> h^{(t)}</script>
2. 区别
1. 对memory 的控制
LSTM: 用output gate 控制,传输给下一个unit
GRU:直接传递给下一个unit,不做任何控制
2. input gate 和reset gate 作用位置不同
LSTM: 计算new memory c^(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-41">\hat{c}^{(t)}</script>时 不对上一时刻的信息做任何控制,而是用forget gate 独立的实现这一点
GRU: 计算new memory h^(t) <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-42">\hat{h}^{(t)}</script> 时利用reset gate 对上一时刻的信息 进行控制。
3. 相似
最大的相似之处就是, 在从t 到 t-1 的更新时都引入了加法。
这个加法的好处在于能防止梯度弥散,因此LSTM和GRU都比一般的RNN效果更好。
Reference:
1. https://cs224d.stanford.edu/lecture_notes/LectureNotes4.pdf
2. Empirical Evaluation of Gated Recurrent Neural Networks on Sequence Modeling
3. https://feature.engineering/difference-between-lstm-and-gru-for-rnns/
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容

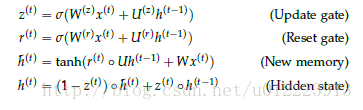
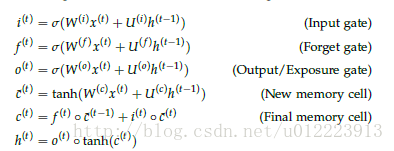








所有评论(0)