【官方】Paddle2.1实现视频理解优化模型 -- PP-TSM
本项目将带大家深入理解TSM的优化模型PP-TSM,从精度优化tricks方面进行详解。同时,实践部分将实现基于PP-TSM在UCF101数据集上从训练到推理全流程实现视频分类。
资源
⭐ ⭐ ⭐ 欢迎点个小小的Star支持!⭐ ⭐ ⭐
开源不易,希望大家多多支持~

-
更多CV和NLP中的transformer模型(BERT、ERNIE、ViT、DeiT、Swin Transformer等)、深度学习资料,请参考:awesome-DeepLearning
-
更多视频模型(PP-TSM、PP-TSN、TimeSformer、BMN等),请参考:PaddleVideo
1. 实验介绍
1.1 实验目的
- 理解并掌握TSM的改进模型PP-TSM的模型优化点;
- 熟悉如何基于飞桨开源框架构建PP-TSM模型,并进行模型训练、评估及推理等流程。
1.2 实验内容
随着互联网上视频的规模日益庞大,人们急切需要研究视频相关算法帮助人们更加容易地找到感兴趣内容的视频。而视频分类算法能够实现自动分析视频所包含的语义信息、理解其内容,对视频进行自动标注、分类和描述,达到与人媲美的准确率。视频分类是继图像分类问题后下一个急需解决的关键任务。
视频分类的主要目标是理解视频中包含的内容,确定视频对应的几个关键主题。视频分类(Video Classification)算法将基于视频的语义内容如人类行为和复杂事件等,将视频片段自动分类至单个或多个类别。视频分类不仅仅是要理解视频中的每一帧图像,更重要的是要识别出能够描述视频的少数几个最佳关键主题。本实验将在视频分类数据集上给大家介绍经典的视频分类模型 TSM 的优化版本 PP-TSM。
1.3 实验环境
本实验使用aistudio至尊版GPU,cuda版本为10.1,具体依赖如下:
- paddlepaddle-gpu==2.2.1.post101
!python -m pip install paddlepaddle-gpu==2.2.1.post101 -f https://paddlepaddle.org.cn/whl/mkl/stable.html
Looking in indexes: https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
Looking in links: https://paddlepaddle.org.cn/whl/mkl/stable.html
Requirement already satisfied: paddlepaddle-gpu==2.2.1.post101 in /opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages (2.2.1.post101)
Requirement already satisfied: six in /opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from paddlepaddle-gpu==2.2.1.post101) (1.16.0)
Requirement already satisfied: requests>=2.20.0 in /opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from paddlepaddle-gpu==2.2.1.post101) (2.22.0)
Requirement already satisfied: Pillow in /opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from paddlepaddle-gpu==2.2.1.post101) (7.1.2)
Requirement already satisfied: decorator in /opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from paddlepaddle-gpu==2.2.1.post101) (4.4.2)
Requirement already satisfied: protobuf>=3.1.0 in /opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from paddlepaddle-gpu==2.2.1.post101) (3.14.0)
Requirement already satisfied: astor in /opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from paddlepaddle-gpu==2.2.1.post101) (0.8.1)
Requirement already satisfied: numpy>=1.13; python_version >= "3.5" and platform_system != "Windows" in /opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from paddlepaddle-gpu==2.2.1.post101) (1.20.3)
Requirement already satisfied: certifi>=2017.4.17 in /opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from requests>=2.20.0->paddlepaddle-gpu==2.2.1.post101) (2019.9.11)
Requirement already satisfied: urllib3!=1.25.0,!=1.25.1,<1.26,>=1.21.1 in /opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from requests>=2.20.0->paddlepaddle-gpu==2.2.1.post101) (1.25.6)
Requirement already satisfied: chardet<3.1.0,>=3.0.2 in /opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from requests>=2.20.0->paddlepaddle-gpu==2.2.1.post101) (3.0.4)
Requirement already satisfied: idna<2.9,>=2.5 in /opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from requests>=2.20.0->paddlepaddle-gpu==2.2.1.post101) (2.8)
1.4 实验设计
实现方案如 图2 所示,对于一条输入的视频数据,首先使用卷积网络提取特征,获取特征表示;然后使用分类器获取属于每类视频动作的概率值。在训练阶段,通过模型输出的概率值与样本的真实标签构建损失函数,从而进行模型训练;在推理阶段,选出概率最大的类别作为最终的输出。
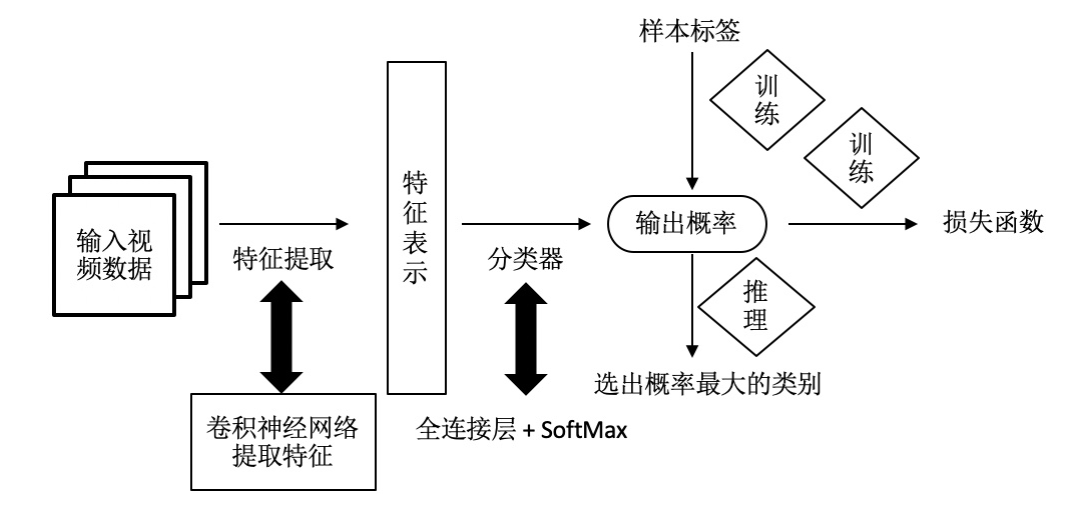
图2 实现方案
2. 实现流程
视频分类任务实现流程主要分为以下7个部分:
- 数据准备:根据网络接收的数据格式,完成相应的预处理操作,保证模型正常读取;
- 模型构建:视频分类模型构建;
- 训练配置:实例化模型,指定模型采用的寻解算法(优化器);
- 模型训练:执行多轮训练不断调整参数,以达到较好的效果;
- 模型保存:保存模型参数;
- 模型评估:对训练好的模型进行评估测试,观察准确率和损失变化;
- 模型推理:使用一条视频数据验证模型分类效果;
2.1 数据准备
2.1.1 数据集简介
UCF101数据集 是一个动作识别数据集,包含现实的动作视频,从 YouTube 上收集,有 101 个动作类别。该数据集是 UCF50 数据集的扩展,该数据集有 50 个动作类别。从 101 个动作类的 13320 个视频中,UCF101 给出了最大的多样性,并且在摄像机运动、物体外观和姿态、物体尺度、视点、杂乱背景、光照条件等方面存在较大的差异,这是目前极具挑战性的数据。
由于大多数可用的动作识别数据集都不现实,而且是由参与者进行的,UCF101 旨在通过学习和探索新的现实行动类别来鼓励进一步研究行动识别。
101 个动作类的视频中,动作类别可以分为5类,如图3中5种颜色的标注:
- Human-Object Interaction
- Body-Motion Only
- Human-Human Interaction
- Playing Musical Instruments
- Sports

图3 UCF101数据集
2.1.2 数据文件简介
将UCF101数据集解压存放在 ucf101 目录下,文件组织形式如下所示:
├── ucf101_{train,val}_videos.txt
├── ucf101
│ ├── ApplyEyeMakeup
│ │ ├── v_ApplyEyeMakeup_g01_c01.avi
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── YoYo
│ │ ├── v_YoYo_g25_c05.avi
│ │ └── ...
│ └── ...
其中,ucf101_{train,val}_videos.txt 中存放的是视频信息,部分内容展示如下:
./ucf101/ApplyEyeMakeup/v_ApplyEyeMakeup_g08_c01 0
./ucf101/ApplyEyeMakeup/v_ApplyEyeMakeup_g08_c02 0
./ucf101/ApplyEyeMakeup/v_ApplyEyeMakeup_g08_c03 0
第一个元素表示视频文件路径,第二个元素表示该视频文件对应的类别。
# 仅在第一次运行代码时使用
# 如不能正常运行,请将路径更新为data目录下的对应路径
!unzip -oq /home/aistudio/data/data105621/UCF101.zip
!mv UCF-101/ ucf101/
2.1.3 数据预处理
import os
import sys
import cv2
import time
import math
import copy
import paddle
import random
import traceback
import itertools
import numpy as np
import os.path as osp
import paddle.nn as nn
import paddle.nn.functional as F
import paddle.nn.initializer as init
from PIL import Image
from tqdm import tqdm
from paddle import ParamAttr
from paddle.optimizer.lr import *
from collections import OrderedDict
from collections.abc import Sequence
from paddle.regularizer import L2Decay
from paddle.nn import (Conv2D, BatchNorm2D, Linear, Dropout, MaxPool2D,
AvgPool2D, AdaptiveAvgPool2D)
将视频解码为帧
class VideoDecoder(object):
"""
Decode mp4 file to frames.
Args:
filepath: the file path of mp4 file
"""
def __init__(self):
pass
def __call__(self, results):
"""
Perform mp4 decode operations.
return:
List where each item is a numpy array after decoder.
"""
file_path = results['filename']
results['format'] = 'video'
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(file_path)
videolen = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
sampledFrames = []
for i in range(videolen):
ret, frame = cap.read()
# maybe first frame is empty
if ret == False:
continue
img = frame[:, :, ::-1]
sampledFrames.append(img)
results['frames'] = sampledFrames
results['frames_len'] = len(sampledFrames)
return results
帧采样
对一段视频进行分段采样,大致流程为:
- 对视频进行分段;
- 从每段视频随机选取一个起始位置;
- 从选取的起始位置采集连续的k帧。
class Sampler(object):
"""
Sample frames id.
NOTE: Use PIL to read image here, has diff with CV2
Args:
num_seg(int): number of segments.
seg_len(int): number of sampled frames in each segment.
valid_mode(bool): True or False.
"""
def __init__(self,
num_seg,
seg_len,
valid_mode=False):
self.num_seg = num_seg
self.seg_len = seg_len
self.valid_mode = valid_mode
def _get(self, frames_idx, results):
data_format = results['format']
if data_format == 'video':
frames = np.array(results['frames'])
imgs = []
for idx in frames_idx:
imgbuf = frames[idx]
img = Image.fromarray(imgbuf, mode='RGB')
imgs.append(img)
results['imgs'] = imgs
return results
def __call__(self, results):
frames_len = int(results['frames_len'])
average_dur = int(frames_len / self.num_seg)
frames_idx = []
for i in range(self.num_seg):
idx = 0
if not self.valid_mode:
if average_dur >= self.seg_len:
# !!!!!!!
idx = random.randint(0, average_dur - self.seg_len)
#idx = 0
idx += i * average_dur
elif average_dur >= 1:
idx += i * average_dur
else:
idx = i
else:
if average_dur >= self.seg_len:
idx = (average_dur - 1) // 2
idx += i * average_dur
elif average_dur >= 1:
idx += i * average_dur
else:
idx = i
for jj in range(idx, idx + self.seg_len):
if results['format'] == 'video':
frames_idx.append(int(jj % frames_len))
else:
raise NotImplementedError
return self._get(frames_idx, results)
图片尺度化
图片尺度化的目的是将图片中短边 resize 到固定的尺寸,图片中的长边按照等比例进行缩放。
class Scale(object):
"""
Scale images.
Args:
short_size(float | int): Short size of an image will be scaled to the short_size.
fixed_ratio(bool): Set whether to zoom according to a fixed ratio. default: True
do_round(bool): Whether to round up when calculating the zoom ratio. default: False
backend(str): Choose pillow or cv2 as the graphics processing backend. default: 'pillow'
"""
def __init__(self,
short_size,
fixed_ratio=True,
do_round=False):
self.short_size = short_size
self.fixed_ratio = fixed_ratio
self.do_round = do_round
def __call__(self, results):
"""
Performs resize operations.
Args:
imgs (Sequence[PIL.Image]): List where each item is a PIL.Image.
For example, [PIL.Image0, PIL.Image1, PIL.Image2, ...]
return:
resized_imgs: List where each item is a PIL.Image after scaling.
"""
imgs = results['imgs']
resized_imgs = []
for i in range(len(imgs)):
img = imgs[i]
w, h = img.size
if (w <= h and w == self.short_size) or (h <= w
and h == self.short_size):
resized_imgs.append(img)
continue
if w < h:
ow = self.short_size
if self.fixed_ratio:
oh = int(self.short_size * 4.0 / 3.0)
else:
oh = int(round(h * self.short_size /
w)) if self.do_round else int(
h * self.short_size / w)
else:
oh = self.short_size
if self.fixed_ratio:
ow = int(self.short_size * 4.0 / 3.0)
else:
ow = int(round(w * self.short_size /
h)) if self.do_round else int(
w * self.short_size / h)
resized_imgs.append(img.resize((ow, oh), Image.BILINEAR))
results['imgs'] = resized_imgs
return results
多尺度剪裁
从多个尺度中随机选择一个裁剪尺度,并计算具体裁剪起始位置以及宽和高,之后从原图中裁剪出随机的固定区域。
class MultiScaleCrop(object):
"""
Random crop images in with multiscale sizes
Args:
target_size(int): Random crop a square with the target_size from an image.
scales(int): List of candidate cropping scales.
max_distort(int): Maximum allowable deformation combination distance.
fix_crop(int): Whether to fix the cutting start point.
allow_duplication(int): Whether to allow duplicate candidate crop starting points.
more_fix_crop(int): Whether to allow more cutting starting points.
"""
def __init__(
self,
target_size, # NOTE: named target size now, but still pass short size in it!
scales=None,
max_distort=1,
fix_crop=True,
allow_duplication=False,
more_fix_crop=True):
self.target_size = target_size
self.scales = scales if scales else [1, .875, .75, .66]
self.max_distort = max_distort
self.fix_crop = fix_crop
self.allow_duplication = allow_duplication
self.more_fix_crop = more_fix_crop
def __call__(self, results):
"""
Performs MultiScaleCrop operations.
Args:
imgs: List where wach item is a PIL.Image.
XXX:
results:
"""
imgs = results['imgs']
input_size = [self.target_size, self.target_size]
im_size = imgs[0].size
# get random crop offset
def _sample_crop_size(im_size):
image_w, image_h = im_size[0], im_size[1]
base_size = min(image_w, image_h)
crop_sizes = [int(base_size * x) for x in self.scales]
crop_h = [
input_size[1] if abs(x - input_size[1]) < 3 else x
for x in crop_sizes
]
crop_w = [
input_size[0] if abs(x - input_size[0]) < 3 else x
for x in crop_sizes
]
pairs = []
for i, h in enumerate(crop_h):
for j, w in enumerate(crop_w):
if abs(i - j) <= self.max_distort:
pairs.append((w, h))
# !!!!!!!
crop_pair = random.choice(pairs)
#crop_pair = pairs[0]
if not self.fix_crop:
# !!!!!!!
w_offset = random.randint(0, image_w - crop_pair[0])
h_offset = random.randint(0, image_h - crop_pair[1])
#w_offset = 0
#h_offset = 0
else:
w_step = (image_w - crop_pair[0]) / 4
h_step = (image_h - crop_pair[1]) / 4
ret = list()
ret.append((0, 0)) # upper left
if self.allow_duplication or w_step != 0:
ret.append((4 * w_step, 0)) # upper right
if self.allow_duplication or h_step != 0:
ret.append((0, 4 * h_step)) # lower left
if self.allow_duplication or (h_step != 0 and w_step != 0):
ret.append((4 * w_step, 4 * h_step)) # lower right
if self.allow_duplication or (h_step != 0 or w_step != 0):
ret.append((2 * w_step, 2 * h_step)) # center
if self.more_fix_crop:
ret.append((0, 2 * h_step)) # center left
ret.append((4 * w_step, 2 * h_step)) # center right
ret.append((2 * w_step, 4 * h_step)) # lower center
ret.append((2 * w_step, 0 * h_step)) # upper center
ret.append((1 * w_step, 1 * h_step)) # upper left quarter
ret.append((3 * w_step, 1 * h_step)) # upper right quarter
ret.append((1 * w_step, 3 * h_step)) # lower left quarter
ret.append((3 * w_step, 3 * h_step)) # lower righ quarter
# !!!!!!!
#w_offset, h_offset = ret[0]
w_offset, h_offset = random.choice(ret)
return crop_pair[0], crop_pair[1], w_offset, h_offset
crop_w, crop_h, offset_w, offset_h = _sample_crop_size(im_size)
crop_img_group = [
img.crop((offset_w, offset_h, offset_w + crop_w, offset_h + crop_h))
for img in imgs
]
ret_img_group = [
img.resize((input_size[0], input_size[1]), Image.BILINEAR)
for img in crop_img_group
]
results['imgs'] = ret_img_group
return results
随机翻转
class RandomFlip(object):
"""
Random Flip images.
Args:
p(float): Random flip images with the probability p.
"""
def __init__(self, p=0.5):
self.p = p
def __call__(self, results):
"""
Performs random flip operations.
Args:
imgs: List where each item is a PIL.Image.
For example, [PIL.Image0, PIL.Image1, PIL.Image2, ...]
return:
flip_imgs: List where each item is a PIL.Image after random flip.
"""
imgs = results['imgs']
# !!!!!!
v = random.random()
#v = 0
if v < self.p:
results['imgs'] = [
img.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT) for img in imgs
]
else:
results['imgs'] = imgs
return results
数据格式转换
将数据格式由PIL.Image转换为Numpy。
class Image2Array(object):
"""
transfer PIL.Image to Numpy array and transpose dimensions from 'dhwc' to 'dchw'.
Args:
transpose: whether to transpose or not, default True, False for slowfast.
"""
def __init__(self, transpose=True):
self.transpose = transpose
def __call__(self, results):
"""
Performs Image to NumpyArray operations.
Args:
imgs: List where each item is a PIL.Image.
For example, [PIL.Image0, PIL.Image1, PIL.Image2, ...]
return:
np_imgs: Numpy array.
"""
imgs = results['imgs']
np_imgs = (np.stack(imgs)).astype('float32')
if self.transpose:
np_imgs = np_imgs.transpose(0, 3, 1, 2) # tchw
results['imgs'] = np_imgs
return results
归一化
class Normalization(object):
"""
Normalization.
Args:
mean(Sequence[float]): mean values of different channels.
std(Sequence[float]): std values of different channels.
tensor_shape(list): size of mean, default [3,1,1]. For slowfast, [1,1,1,3]
"""
def __init__(self, mean, std, tensor_shape=[3, 1, 1]):
if not isinstance(mean, Sequence):
raise TypeError(
f'Mean must be list, tuple or np.ndarray, but got {type(mean)}')
if not isinstance(std, Sequence):
raise TypeError(
f'Std must be list, tuple or np.ndarray, but got {type(std)}')
self.mean = np.array(mean).reshape(tensor_shape).astype(np.float32)
self.std = np.array(std).reshape(tensor_shape).astype(np.float32)
def __call__(self, results):
"""
Performs normalization operations.
Args:
imgs: Numpy array.
return:
np_imgs: Numpy array after normalization.
"""
imgs = results['imgs']
norm_imgs = imgs / 255.0
norm_imgs -= self.mean
norm_imgs /= self.std
results['imgs'] = norm_imgs
return results
随机剪裁
class RandomCrop(object):
"""
Random crop images.
Args:
target_size(int): Random crop a square with the target_size from an image.
"""
def __init__(self, target_size):
self.target_size = target_size
def __call__(self, results):
"""
Performs random crop operations.
Args:
imgs: List where each item is a PIL.Image.
For example, [PIL.Image0, PIL.Image1, PIL.Image2, ...]
return:
crop_imgs: List where each item is a PIL.Image after random crop.
"""
imgs = results['imgs']
if 'backend' in results and results['backend'] == 'pyav': # [c,t,h,w]
h, w = imgs.shape[2:]
else:
w, h = imgs[0].size
th, tw = self.target_size, self.target_size
assert (w >= self.target_size) and (h >= self.target_size), \
"image width({}) and height({}) should be larger than crop size".format(
w, h, self.target_size)
crop_images = []
if 'backend' in results and results['backend'] == 'pyav':
x1 = np.random.randint(0, w - tw)
y1 = np.random.randint(0, h - th)
crop_images = imgs[:, :, y1:y1 + th, x1:x1 + tw] # [C, T, th, tw]
else:
x1 = random.randint(0, w - tw)
y1 = random.randint(0, h - th)
for img in imgs:
if w == tw and h == th:
crop_images.append(img)
else:
crop_images.append(img.crop((x1, y1, x1 + tw, y1 + th)))
results['imgs'] = crop_images
return results
中心剪裁
中心裁剪与随机裁剪类似,具体的差异在于选取裁剪起始点的方法不同。
class CenterCrop(object):
"""
Center crop images.
Args:
target_size(int): Center crop a square with the target_size from an image.
do_round(bool): Whether to round up the coordinates of the upper left corner of the cropping area. default: True
"""
def __init__(self, target_size, do_round=True):
self.target_size = target_size
self.do_round = do_round
def __call__(self, results):
"""
Performs Center crop operations.
Args:
imgs: List where each item is a PIL.Image.
For example, [PIL.Image0, PIL.Image1, PIL.Image2, ...]
return:
ccrop_imgs: List where each item is a PIL.Image after Center crop.
"""
imgs = results['imgs']
ccrop_imgs = []
for img in imgs:
w, h = img.size
th, tw = self.target_size, self.target_size
assert (w >= self.target_size) and (h >= self.target_size), \
"image width({}) and height({}) should be larger than crop size".format(
w, h, self.target_size)
x1 = int(round((w - tw) / 2.0)) if self.do_round else (w - tw) // 2
y1 = int(round((h - th) / 2.0)) if self.do_round else (h - th) // 2
ccrop_imgs.append(img.crop((x1, y1, x1 + tw, y1 + th)))
results['imgs'] = ccrop_imgs
return results
数据增强方式Mixup
class Mixup(object):
"""
Mixup operator.
Args:
alpha(float): alpha value.
"""
def __init__(self, alpha=0.2):
assert alpha > 0., \
'parameter alpha[%f] should > 0.0' % (alpha)
self.alpha = alpha
def __call__(self, batch):
imgs, labels = list(zip(*batch))
imgs = np.array(imgs)
labels = np.array(labels)
bs = len(batch)
idx = np.random.permutation(bs)
lam = np.random.beta(self.alpha, self.alpha)
lams = np.array([lam] * bs, dtype=np.float32)
imgs = lam * imgs + (1 - lam) * imgs[idx]
return list(zip(imgs, labels, labels[idx], lams))
2.1.4 数据预处理模块组合
为方便对数据进行组合处理,将训练模式和验证模式下的数据预处理模块进行封装。
class Compose(object):
"""
Composes several pipelines(include decode func, sample func, and transforms) together.
Note: To deal with ```list```type cfg temporaray, like:
transform:
- Crop: # A list
attribute: 10
- Resize: # A list
attribute: 20
every key of list will pass as the key name to build a module.
XXX: will be improved in the future.
Args:
pipelines (list): List of transforms to compose.
Returns:
A compose object which is callable, __call__ for this Compose
object will call each given :attr:`transforms` sequencely.
"""
def __init__(self, train_mode=False):
# assert isinstance(pipelines, Sequence)
self.pipelines = list()
self.pipelines.append(VideoDecoder())
if train_mode:
self.pipelines.append(Sampler(num_seg=8, seg_len=1, valid_mode=False))
#self.pipelines.append(MultiScaleCrop(target_size=224, allow_duplication=True))
self.pipelines.append(MultiScaleCrop(target_size=256))
self.pipelines.append(RandomCrop(target_size=224))
self.pipelines.append(RandomFlip())
else:
self.pipelines.append(Sampler(num_seg=8, seg_len=1, valid_mode=True))
self.pipelines.append(Scale(short_size=256, fixed_ratio=False))
self.pipelines.append(CenterCrop(target_size=224))
self.pipelines.append(Image2Array())
self.pipelines.append(Normalization(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]))
def __call__(self, data):
# 将传入的 data 依次经过 pipelines 中对象处理
for p in self.pipelines:
try:
data = p(data)
except Exception as e:
stack_info = traceback.format_exc()
print("fail to perform transform [{}] with error: "
"{} and stack:\n{}".format(p, e, str(stack_info)))
raise e
return data
2.1.5 数据读取
接下来我们通过继承paddle的Dataset API来构建一个数据读取器,方便每次从数据中获取一个样本和对应的标签。
class VideoDataset(paddle.io.Dataset):
"""Video dataset for action recognition
The dataset loads raw videos and apply specified transforms on them.
The index file is a file with multiple lines, and each line indicates
a sample video with the filepath and label, which are split with a whitesapce.
Example of a inde file:
.. code-block:: txt
path/000.mp4 1
path/001.mp4 1
path/002.mp4 2
path/003.mp4 2
Args:
file_path(str): Path to the index file.
pipeline(XXX): A sequence of data transforms.
**kwargs: Keyword arguments for ```BaseDataset```.
"""
def __init__(self, file_path, pipeline, num_retries=5, suffix='', test_mode=False):
super().__init__()
self.file_path = file_path
self.pipeline = pipeline
self.num_retries = num_retries
self.suffix = suffix
self.info = self.load_file()
self.test_mode = test_mode
def load_file(self):
"""Load index file to get video information."""
info = []
with open(self.file_path, 'r') as fin:
for line in fin:
line_split = line.strip().split()
filename, labels = line_split
filename = filename + self.suffix
info.append(dict(filename=filename, labels=int(labels)))
return info
def prepare_train(self, idx):
"""TRAIN & VALID. Prepare the data for training/valid given the index."""
#Try to catch Exception caused by reading corrupted video file
for ir in range(self.num_retries):
try:
results = copy.deepcopy(self.info[idx])
results = self.pipeline(results)
except Exception as e:
if ir < self.num_retries - 1:
print(
"Error when loading {}, have {} trys, will try again".
format(results['filename'], ir))
idx = random.randint(0, len(self.info) - 1)
continue
return results['imgs'], np.array([results['labels']])
def prepare_test(self, idx):
"""TEST. Prepare the data for test given the index."""
#Try to catch Exception caused by reading corrupted video file
for ir in range(self.num_retries):
try:
results = copy.deepcopy(self.info[idx])
results = self.pipeline(results)
except Exception as e:
if ir < self.num_retries - 1:
print(
"Error when loading {}, have {} trys, will try again".
format(results['filename'], ir))
idx = random.randint(0, len(self.info) - 1)
continue
return results['imgs'], np.array([results['labels']])
def __len__(self):
"""get the size of the dataset."""
return len(self.info)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
""" Get the sample for either training or testing given index"""
if self.test_mode:
return self.prepare_test(idx)
else:
return self.prepare_train(idx)
def build_dataloader(dataset,
batch_size,
num_workers,
train_mode,
places,
shuffle=True,
drop_last=True,
collate_fn_cfg=None):
"""Build Paddle Dataloader.
XXX explain how the dataloader work!
Args:
dataset (paddle.dataset): A PaddlePaddle dataset object.
batch_size (int): batch size on single card.
num_worker (int): num_worker
shuffle(bool): whether to shuffle the data at every epoch.
"""
sampler = paddle.io.DistributedBatchSampler(dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=shuffle,
drop_last=drop_last)
#NOTE(shipping): when switch the mix operator on, such as: mixup, cutmix.
# batch like: [[img, label, attibute, ...], [imgs, label, attribute, ...], ...] will recollate to:
# [[img, img, ...], [label, label, ...], [attribute, attribute, ...], ...] as using numpy.transpose.
def mix_collate_fn(batch):
pipeline = collate_fn_cfg
batch = pipeline(batch)
slots = []
for items in batch:
for i, item in enumerate(items):
if len(slots) < len(items):
slots.append([item])
else:
slots[i].append(item)
return [np.stack(slot, axis=0) for slot in slots]
data_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(
dataset,
batch_sampler=sampler,
places=places,
num_workers=num_workers,
collate_fn=mix_collate_fn if collate_fn_cfg is not None else None,
return_list=True)
return data_loader
2.2 模型构建
2.2.1 PP-TSM 简介
背景
相较于图像,视频具有额外的时间维度信息,因此如何更好的利用视频中的时序信息是视频研究的重点。目前常用的方法有三类:
- 使用RNN对视频特征进行时序建模,如AttentionLSTM模型。这类模型的输入是视频特征,而不是原始视频,因此往往用作后处理模块。
- 使用3D网络提取时序信息。如SlowFast模型,使用Slow和Fast两个网络分支分别捕获视频中的表观信息和运动信息,该模型在视频分类任务上取得了SOTA的效果,同时是AVA 视频检测挑战赛的冠军模型。
- 使用2D网络提取时序信息,如经典的TSN和TSM模型。相较于TSN模型,TSM模型使用时序位移模块对时序信息建模,在不增加计算量的前提下提升网络的精度,非常适合工业落地。
PP-TSM模型在基本不增加计算量的前提下,使用Kinetics-400数据集训练的精度可以提升到76.16%,超过同等Backbone下3D模型SlowFast,且推理速度快4.5倍,具有显著的性能优势。
精度优化Tricks详解
- 数据增强Video Mix-up
Mix-up是图像领域常用的数据增广方法,它将两幅图像以一定的权值叠加构成新的输入图像。对于视频Mix-up,即是将两个视频以一定的权值叠加构成新的输入视频。相较于图像,视频由于多了时间维度,混合的方式可以有更多的选择。实验中,我们对每个视频,首先抽取固定数量的帧,并给每一帧赋予相同的权重,然后与另一个视频叠加作为新的输入视频。结果表明,这种Mix-up方式能有效提升网络在时空上的抗干扰能力。
- 更优的网络结构
Better Backbone:骨干网络可以说是一个模型的基础,一个优秀的骨干网络会给模型的性能带来极大的提升。针对TSM,飞桨研发人员使用更加优异的ResNet50_vd作为模型的骨干网络,在保持原有参数量的同时提升了模型精度。ResNet50_vd是指拥有50个卷积层的ResNet-D网络。如下图所示,ResNet系列网络在被提出后经过了B、C、D三个版本的改进。ResNet-B将Path A中11卷积的stride由2改为1,避免了信息丢失;ResNet-C将第一个77的卷积核调整为3个33卷积核,减少计算量的同时增加了网络非线性;ResNet-D进一步将Path B中11卷积的stride由2改为1,并添加了平均池化层,保留了更多的信息。
Feature aggregation:对TSM模型,在骨干网络提取特征后,还需要使用分类器做特征分类。实验表明,在特征平均之后分类,可以减少frame-level特征的干扰,获得更高的精度。假设输入视频抽取的帧数为N,则经过骨干网络后,可以得到N个frame-level特征。分类器有两种实现方式:第一种是先对N个帧级特征进行平均,得到视频级特征后,再用全连接层进行分类;另一种方式是先接全连接层,得到N个权重后进行平均。飞桨开发人员经过大量实验验证发现,采用第1种方式有更好的精度收益。
- 更稳定的训练策略
Cosine decay LR:在使用梯度下降算法优化目标函数时,我们使用余弦退火策略调整学习率。同时使用Warm-up策略,在模型训练之初选用较小的学习率,训练一段时间之后再使用预设的学习率训练,这使得收敛过程更加快速平滑。
Scale fc learning rate:在训练过程中,我们给全连接层设置的学习率为其它层的5倍。实验结果表明,通过给分类器层设置更大的学习率,有助于网络更好的学习收敛,提升模型精度。
- Label smooth
标签平滑是一种对分类器层进行正则化的机制,通过在真实的分类标签one-hot编码中真实类别的1上减去一个小量,非真实标签的0上加上一个小量,将硬标签变成一个软标签,达到正则化的作用,防止过拟合,提升模型泛化能力。
- Precise BN
假定训练数据的分布和测试数据的分布是一致的,对于Batch Normalization层,通常在训练过程中会计算滑动均值和滑动方差,供测试时使用。但滑动均值并不等于真实的均值,因此测试时的精度仍会受到一定影响。为了获取更加精确的均值和方差供BN层在测试时使用,在实验中,我们会在网络训练完一个Epoch后,固定住网络中的参数不动,然后将训练数据输入网络做前向计算,保存下来每个step的均值和方差,最终得到所有训练样本精确的均值和方差,提升测试精度。
- 知识蒸馏方案:Two Stages Knowledge Distillation
我们使用两阶段知识蒸馏方案提升模型精度。第一阶段使用半监督标签知识蒸馏方法对图像分类模型进行蒸馏,以获得具有更好分类效果的pretrain模型。第二阶段使用更高精度的视频分类模型作为教师模型进行蒸馏,以进一步提升模型精度。实验中,将以ResNet152为Backbone的CSN模型作为第二阶段蒸馏的教师模型,在uniform和dense评估策略下,精度均可以提升大约0.6个点。最终PP-TSM精度达到76.16,超过同等Backbone下的SlowFast模型。
2.2.2 代码实现
class ConvBNLayer(nn.Layer):
"""Conv2D and BatchNorm2D layer.
Args:
in_channels (int): Number of channels for the input.
out_channels (int): Number of channels for the output.
kernel_size (int): Kernel size.
stride (int): Stride in the Conv2D layer. Default: 1.
groups (int): Groups in the Conv2D, Default: 1.
is_tweaks_mode (bool): switch for tweaks. Default: False.
act (str): Indicate activation after BatchNorm2D layer.
name (str): the name of an instance of ConvBNLayer.
Note: weight and bias initialization include initialize values and name the restored parameters, values initialization are explicit declared in the ```init_weights```method.
"""
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size,
stride=1,
groups=1,
is_tweaks_mode=False,
act=None,
name=None):
super(ConvBNLayer, self).__init__()
self.is_tweaks_mode = is_tweaks_mode
#ResNet-D 1/2:add a 2×2 average pooling layer with a stride of 2 before the convolution,
# whose stride is changed to 1, works well in practice.
self._pool2d_avg = AvgPool2D(kernel_size=2,
stride=2,
padding=0,
ceil_mode=True)
self._conv = Conv2D(in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride,
padding=(kernel_size - 1) // 2,
groups=groups,
weight_attr=ParamAttr(name=name + "_weights"),
bias_attr=False)
if name == "conv1":
bn_name = "bn_" + name
else:
bn_name = "bn" + name[3:]
self._act = act
self._batch_norm = BatchNorm2D(
out_channels,
weight_attr=ParamAttr(name=bn_name + "_scale",
regularizer=L2Decay(0.0)),
bias_attr=ParamAttr(bn_name + "_offset", regularizer=L2Decay(0.0)))
def forward(self, inputs):
if self.is_tweaks_mode:
inputs = self._pool2d_avg(inputs)
y = self._conv(inputs)
y = self._batch_norm(y)
if self._act:
y = getattr(paddle.nn.functional, self._act)(y)
return y
class BottleneckBlock(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
stride,
shortcut=True,
if_first=False,
num_seg=8,
name=None):
super(BottleneckBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv0 = ConvBNLayer(in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=1,
act="leaky_relu",
name=name + "_branch2a")
self.conv1 = ConvBNLayer(in_channels=out_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=3,
stride=stride,
act="leaky_relu",
name=name + "_branch2b")
self.conv2 = ConvBNLayer(in_channels=out_channels,
out_channels=out_channels * 4,
kernel_size=1,
act=None,
name=name + "_branch2c")
if not shortcut:
self.short = ConvBNLayer(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=out_channels * 4,
kernel_size=1,
stride=
1, #ResNet-D 2/2:add a 2×2 average pooling layer with a stride of 2 before the convolution,
# whose stride is changed to 1, works well in practice.
is_tweaks_mode=False if if_first else True,
name=name + "_branch1")
self.shortcut = shortcut
self.num_seg = num_seg
def forward(self, inputs):
shifts = paddle.fluid.layers.temporal_shift(inputs, self.num_seg,
1.0 / self.num_seg)
y = self.conv0(shifts)
conv1 = self.conv1(y)
conv2 = self.conv2(conv1)
if self.shortcut:
short = inputs
else:
short = self.short(inputs)
y = paddle.add(x=short, y=conv2)
return F.leaky_relu(y)
class BasicBlock(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
stride,
shortcut=True,
name=None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.stride = stride
self.conv0 = ConvBNLayer(in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
filter_size=3,
stride=stride,
act="leaky_relu",
name=name + "_branch2a")
self.conv1 = ConvBNLayer(in_channels=out_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
filter_size=3,
act=None,
name=name + "_branch2b")
if not shortcut:
self.short = ConvBNLayer(in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
filter_size=1,
stride=stride,
name=name + "_branch1")
self.shortcut = shortcut
def forward(self, inputs):
y = self.conv0(inputs)
conv1 = self.conv1(y)
if self.shortcut:
short = inputs
else:
short = self.short(inputs)
y = paddle.add(short, conv1)
y = F.leaky_relu(y)
return y
class ResNetTweaksTSM(nn.Layer):
"""ResNet TSM backbone.
Args:
depth (int): Depth of resnet model.
pretrained (str): pretrained model. Default: None.
"""
def __init__(self, depth, num_seg=8, pretrained=None):
super(ResNetTweaksTSM, self).__init__()
self.pretrained = pretrained
self.layers = depth
self.num_seg = num_seg
supported_layers = [18, 34, 50, 101, 152]
assert self.layers in supported_layers, \
"supported layers are {} but input layer is {}".format(
supported_layers, self.layers)
if self.layers == 18:
depth = [2, 2, 2, 2]
elif self.layers == 34 or self.layers == 50:
depth = [3, 4, 6, 3]
elif self.layers == 101:
depth = [3, 4, 23, 3]
elif self.layers == 152:
depth = [3, 8, 36, 3]
in_channels = 64
out_channels = [64, 128, 256, 512]
#ResNet-C: use three 3x3 conv, replace, one 7x7 conv
self.conv1_1 = ConvBNLayer(in_channels=3,
out_channels=32,
kernel_size=3,
stride=2,
act='leaky_relu',
name="conv1_1")
self.conv1_2 = ConvBNLayer(in_channels=32,
out_channels=32,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
act='leaky_relu',
name="conv1_2")
self.conv1_3 = ConvBNLayer(in_channels=32,
out_channels=64,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
act='leaky_relu',
name="conv1_3")
self.pool2D_max = MaxPool2D(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.block_list = []
if self.layers >= 50:
for block in range(len(depth)):
shortcut = False
for i in range(depth[block]):
if self.layers in [101, 152] and block == 2:
if i == 0:
conv_name = "res" + str(block + 2) + "a"
else:
conv_name = "res" + str(block + 2) + "b" + str(i)
else:
conv_name = "res" + str(block + 2) + chr(97 + i)
bottleneck_block = self.add_sublayer(
'bb_%d_%d' %
(block, i), #same with PaddleClas, for loading pretrain
BottleneckBlock(
in_channels=in_channels
if i == 0 else out_channels[block] * 4,
out_channels=out_channels[block],
stride=2 if i == 0 and block != 0 else 1,
num_seg=self.num_seg,
shortcut=shortcut,
if_first=block == i == 0,
name=conv_name))
in_channels = out_channels[block] * 4
self.block_list.append(bottleneck_block)
shortcut = True
else:
for block in range(len(depth)):
shortcut = False
for i in range(depth[block]):
conv_name = "res" + str(block + 2) + chr(97 + i)
basic_block = self.add_sublayer(
conv_name,
BasicBlock(in_channels=in_channels[block]
if i == 0 else out_channels[block],
out_channels=out_channels[block],
stride=2 if i == 0 and block != 0 else 1,
shortcut=shortcut,
name=conv_name))
self.block_list.append(basic_block)
shortcut = True
def init_weights(self):
"""Initiate the parameters.
Note:
1. when indicate pretrained loading path, will load it to initiate backbone.
2. when not indicating pretrained loading path, will follow specific initialization initiate backbone. Always, Conv2D layer will be initiated by KaimingNormal function, and BatchNorm2d will be initiated by Constant function.
Please refer to https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/en/develop/api/paddle/nn/initializer/kaiming/KaimingNormal_en.html
"""
#XXX: check bias!!! check pretrained!!!
if isinstance(self.pretrained, str) and self.pretrained.strip() != "":
load_ckpt(self, self.pretrained)
elif self.pretrained is None or self.pretrained.strip() == "":
for layer in self.sublayers():
if isinstance(layer, nn.Conv2D):
#XXX: no bias
weight_init_(layer, 'KaimingNormal')
elif isinstance(layer, nn.BatchNorm2D):
weight_init_(layer, 'Constant', value=1)
def forward(self, inputs):
"""Define how the backbone is going to run.
"""
#NOTE: Already merge axis 0(batches) and axis 1(channels) before extracting feature phase,
# please refer to paddlevideo/modeling/framework/recognizers/recognizer2d.py#L27
#y = paddle.reshape(
# inputs, [-1, inputs.shape[2], inputs.shape[3], inputs.shape[4]])
####ResNet-C: use three 3x3 conv, replace, one 7x7 conv
y = self.conv1_1(inputs)
y = self.conv1_2(y)
y = self.conv1_3(y)
y = self.pool2D_max(y)
for block in self.block_list:
y = block(y)
return y
class CrossEntropyLoss(nn.Layer):
"""Cross Entropy Loss."""
def __init__(self, loss_weight=1.0):
super().__init__()
self.loss_weight = loss_weight
def _forward(self, score, labels, **kwargs):
"""Forward function.
Args:
score (paddle.Tensor): The class score.
labels (paddle.Tensor): The ground truth labels.
kwargs: Any keyword argument to be used to calculate
CrossEntropy loss.
Returns:
loss (paddle.Tensor): The returned CrossEntropy loss.
"""
loss = F.cross_entropy(score, labels, **kwargs)
return loss
def forward(self, *args, **kwargs):
"""Defines the computation performed at every call.
Args:
*args: The positional arguments for the corresponding
loss.
**kwargs: The keyword arguments for the corresponding
loss.
Returns:
paddle.Tensor: The calculated loss.
"""
return self._forward(*args, **kwargs) * self.loss_weight
class ppTSMHead(nn.Layer):
""" ppTSM Head
Args:
num_classes (int): The number of classes to be classified.
in_channels (int): The number of channles in input feature.
loss_cfg (dict): Config for building config. Default: dict(name='CrossEntropyLoss').
drop_ratio(float): drop ratio. Default: 0.8.
std(float): Std(Scale) value in normal initilizar. Default: 0.001.
kwargs (dict, optional): Any keyword argument to initialize.
"""
def __init__(self,
num_classes,
in_channels,
drop_ratio=0.8,
std=0.01,
data_format="NCHW",
ls_eps=0.):
super().__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.drop_ratio = drop_ratio
self.ls_eps = ls_eps
self.fc = Linear(self.in_channels,
self.num_classes,
weight_attr=ParamAttr(learning_rate=5.0,
regularizer=L2Decay(1e-4)),
bias_attr=ParamAttr(learning_rate=10.0,
regularizer=L2Decay(0.0)))
self.stdv = std
self.loss_func = CrossEntropyLoss()
self.avgpool2d = AdaptiveAvgPool2D((1, 1), data_format=data_format)
self.dropout = Dropout(p=self.drop_ratio)
def init_weights(self):
"""Initiate the FC layer parameters"""
weight_init_(self.fc, 'Normal', 'fc_0.w_0', 'fc_0.b_0', std=self.stdv)
def forward(self, x, seg_num):
"""Define how the head is going to run.
Args:
x (paddle.Tensor): The input data.
num_segs (int): Number of segments.
Returns:
score: (paddle.Tensor) The classification scores for input samples.
"""
#XXX: check dropout location!
# [N * num_segs, in_channels, 7, 7]
x = self.avgpool2d(x)
# [N * num_segs, in_channels, 1, 1]
if self.dropout is not None:
x = self.dropout(x)
# [N * seg_num, in_channels, 1, 1]
x = paddle.reshape(x, [-1, seg_num, x.shape[1]])
# [N, seg_num, in_channels]
x = paddle.mean(x, axis=1)
# [N, in_channels]
x = paddle.reshape(x, shape=[-1, self.in_channels])
# [N, in_channels]
score = self.fc(x)
# [N, num_class]
return score
def loss(self, scores, labels, valid_mode=False, **kwargs):
"""Calculate the loss accroding to the model output ```scores```,
and the target ```labels```.
Args:
scores (paddle.Tensor): The output of the model.
labels (paddle.Tensor): The target output of the model.
Returns:
losses (dict): A dict containing field 'loss'(mandatory) and 'top1_acc', 'top5_acc'(optional).
"""
if len(labels) == 1: #commonly case
labels = labels[0]
losses = dict()
if self.ls_eps != 0. and not valid_mode: # label_smooth
loss = self.label_smooth_loss(scores, labels, **kwargs)
else:
loss = self.loss_func(scores, labels, **kwargs)
top1, top5 = self.get_acc(scores, labels, valid_mode)
losses['top1'] = top1
losses['top5'] = top5
losses['loss'] = loss
return losses
elif len(labels) == 3: # mix_up
labels_a, labels_b, lam = labels
lam = lam[0] # get lam value
losses = dict()
if self.ls_eps != 0:
loss_a = self.label_smooth_loss(scores, labels_a, **kwargs)
loss_b = self.label_smooth_loss(scores, labels_b, **kwargs)
else:
loss_a = self.loss_func(scores, labels_a, **kwargs)
loss_b = self.loss_func(scores, labels_b, **kwargs)
loss = lam * loss_a + (1 - lam) * loss_b
top1a, top5a = self.get_acc(scores, labels_a, valid_mode)
top1b, top5b = self.get_acc(scores, labels_b, valid_mode)
top1 = lam * top1a + (1 - lam) * top1b
top5 = lam * top5a + (1 - lam) * top5b
losses['top1'] = top1
losses['top5'] = top5
losses['loss'] = loss
return losses
else:
raise NotImplemented
def label_smooth_loss(self, scores, labels, **kwargs):
labels = F.one_hot(labels, self.num_classes)
labels = F.label_smooth(labels, epsilon=self.ls_eps)
labels = paddle.squeeze(labels, axis=1)
loss = self.loss_func(scores, labels, soft_label=True, **kwargs)
return loss
def get_acc(self, scores, labels, valid_mode):
top1 = paddle.metric.accuracy(input=scores, label=labels, k=1)
top5 = paddle.metric.accuracy(input=scores, label=labels, k=5)
return top1, top5
Recognizer2D
将主干网络和头部分封装。
class Recognizer2D(nn.Layer):
"""2D recognizer model framework."""
def __init__(self, backbone=None, head=None):
super().__init__()
self.backbone = backbone
self.backbone.init_weights()
self.head = head
self.head.init_weights()
def forward_net(self, imgs):
# NOTE: As the num_segs is an attribute of dataset phase, and didn't pass to build_head phase, should obtain it from imgs(paddle.Tensor) now, then call self.head method.
num_segs = imgs.shape[1] # imgs.shape=[N,T,C,H,W], for most commonly case
imgs = paddle.reshape_(imgs, [-1] + list(imgs.shape[2:]))
feature = self.backbone(imgs)
cls_score = self.head(feature, num_segs)
return cls_score
def train_step(self, data_batch):
"""Define how the model is going to train, from input to output.
"""
imgs = data_batch[0]
labels = data_batch[1:]
cls_score = self.forward_net(imgs)
loss_metrics = self.head.loss(cls_score, labels)
return loss_metrics
def val_step(self, data_batch):
imgs = data_batch[0]
labels = data_batch[1:]
cls_score = self.forward_net(imgs)
loss_metrics = self.head.loss(cls_score, labels, valid_mode=True)
return loss_metrics
def test_step(self, data_batch):
"""Define how the model is going to test, from input to output."""
# NOTE: (shipping) when testing, the net won't call head.loss, we deal with the test processing in /paddlevideo/metrics
imgs = data_batch[0]
cls_score = self.forward_net(imgs)
return cls_score
def infer_step(self, data_batch):
"""Define how the model is going to test, from input to output."""
imgs = data_batch[0]
cls_score = self.forward_net(imgs)
return cls_score
def load_ckpt(model, weight_path):
"""
1. Load pre-trained model parameters
2. Extract and convert from the pre-trained model to the parameters
required by the existing model
3. Load the converted parameters of the existing model
"""
#model.set_state_dict(state_dict)
if not osp.isfile(weight_path):
raise IOError(f'{weight_path} is not a checkpoint file')
#state_dicts = load(weight_path)
state_dicts = paddle.load(weight_path)
tmp = {}
total_len = len(model.state_dict())
with tqdm(total=total_len, position=1, bar_format='{desc}', desc="Loading weights") as desc:
for item in tqdm(model.state_dict(), total=total_len, position=0):
name = item
desc.set_description('Loading %s' % name)
if name not in state_dicts: # Convert from non-parallel model
if str('backbone.' + name) in state_dicts:
tmp[name] = state_dicts['backbone.' + name]
else: # Convert from parallel model
tmp[name] = state_dicts[name]
time.sleep(0.01)
ret_str = "loading {:<20d} weights completed.".format(len(model.state_dict()))
desc.set_description(ret_str)
model.set_state_dict(tmp)
def weight_init_(layer,
func,
weight_name=None,
bias_name=None,
bias_value=0.0,
**kwargs):
"""
In-place params init function.
Usage:
.. code-block:: python
import paddle
import numpy as np
data = np.ones([3, 4], dtype='float32')
linear = paddle.nn.Linear(4, 4)
input = paddle.to_tensor(data)
print(linear.weight)
linear(input)
weight_init_(linear, 'Normal', 'fc_w0', 'fc_b0', std=0.01, mean=0.1)
print(linear.weight)
"""
if hasattr(layer, 'weight') and layer.weight is not None:
getattr(init, func)(**kwargs)(layer.weight)
if weight_name is not None:
# override weight name
layer.weight.name = weight_name
if hasattr(layer, 'bias') and layer.bias is not None:
init.Constant(bias_value)(layer.bias)
if bias_name is not None:
# override bias name
layer.bias.name = bias_name
2.3 训练配置
使用pptsm在Kinetics-400数据集上训练的模型作为预训练模型。
# 仅在第一次运行代码时使用
!wget https://videotag.bj.bcebos.com/PaddleVideo-release2.1/PPTSM/ppTSM_k400_uniform_distill.pdparams
framework = 'Recognizer2D'
# backbone
# name = 'ResNetTweaksTSM'
#pretrained = 'ResNet50_vd_ssld_v2_pretrained.pdparams'
pretrained = 'ppTSM_k400_uniform_distill.pdparams'
depth = 50
# head
num_classes = 101
in_channels = 2048
drop_ratio = 0.5
std = 0.01
ls_eps = 0.1
# DATASET
batch_size = 16
num_workers = 1
test_batch_size = 1
train_file_path = 'ucf101_train_videos.txt'
valid_file_path = 'ucf101_val_videos.txt'
suffix = '.avi'
train_shuffle = True
valid_shuffle = False
# mixup
mix_collate_fn = Mixup(alpha=0.2)
# OPTIMIZER
momentum = 0.9
# lr
max_epoch = 30
warmup_epochs = 5
warmup_start_lr = 0.0005
cosine_base_lr = 0.001
iter_step = True
# PRECISEBN
preciseBN = True
preciseBN_interval = 5
num_iters_preciseBN = 200
model_name = 'ppTSM'
log_interval = 10
save_interval = 3
val_interval = 1
epochs = 30
2.4 模型训练
Color = {
'RED': '\033[31m',
'HEADER': '\033[35m', # deep purple
'PURPLE': '\033[95m', # purple
'OKBLUE': '\033[94m',
'OKGREEN': '\033[92m',
'WARNING': '\033[93m',
'FAIL': '\033[91m',
'ENDC': '\033[0m'
}
def coloring(message, color="OKGREEN"):
assert color in Color.keys()
if os.environ.get('COLORING', True):
return Color[color] + str(message) + Color["ENDC"]
else:
return message
def build_record(framework_type):
record_list = [
("loss", AverageMeter('loss', '7.5f')),
("lr", AverageMeter('lr', 'f', need_avg=False)),
("batch_time", AverageMeter('elapse', '.3f')),
("reader_time", AverageMeter('reader', '.3f')),
]
if 'Recognizer' in framework_type:
record_list.append(("top1", AverageMeter("top1", '.5f')))
record_list.append(("top5", AverageMeter("top5", '.5f')))
record_list = OrderedDict(record_list)
return record_list
def log_batch(metric_list, batch_id, epoch_id, total_epoch, mode, ips):
metric_str = ' '.join([str(m.value) for m in metric_list.values()])
epoch_str = "epoch:[{:>3d}/{:<3d}]".format(epoch_id, total_epoch)
step_str = "{:s} step:{:<4d}".format(mode, batch_id)
print("{:s} {:s} {:s}s {}".format(
coloring(epoch_str, "HEADER") if batch_id == 0 else epoch_str,
coloring(step_str, "PURPLE"), coloring(metric_str, 'OKGREEN'), ips))
def log_epoch(metric_list, epoch, mode, ips):
metric_avg = ' '.join([str(m.mean) for m in metric_list.values()] +
[metric_list['batch_time'].total])
end_epoch_str = "END epoch:{:<3d}".format(epoch)
print("{:s} {:s} {:s}s {}".format(coloring(end_epoch_str, "RED"),
coloring(mode, "PURPLE"),
coloring(metric_avg, "OKGREEN"),
ips))
class AverageMeter(object):
"""
Computes and stores the average and current value
"""
def __init__(self, name='', fmt='f', need_avg=True):
self.name = name
self.fmt = fmt
self.need_avg = need_avg
self.reset()
def reset(self):
""" reset """
self.val = 0
self.avg = 0
self.sum = 0
self.count = 0
def update(self, val, n=1):
""" update """
if isinstance(val, paddle.Tensor):
val = val.numpy()[0]
self.val = val
self.sum += val * n
self.count += n
self.avg = self.sum / self.count
@property
def total(self):
return '{self.name}_sum: {self.sum:{self.fmt}}'.format(self=self)
@property
def total_minute(self):
return '{self.name}_sum: {s:{self.fmt}} min'.format(s=self.sum / 60,
self=self)
@property
def mean(self):
return '{self.name}_avg: {self.avg:{self.fmt}}'.format(
self=self) if self.need_avg else ''
@property
def value(self):
return '{self.name}: {self.val:{self.fmt}}'.format(self=self)
class CustomWarmupCosineDecay(LRScheduler):
"""
We combine warmup and stepwise-cosine which is used in slowfast model.
Args:
warmup_start_lr (float): start learning rate used in warmup stage.
warmup_epochs (int): the number epochs of warmup.
cosine_base_lr (float|int, optional): base learning rate in cosine schedule.
max_epoch (int): total training epochs.
num_iters(int): number iterations of each epoch.
last_epoch (int, optional): The index of last epoch. Can be set to restart training. Default: -1, means initial learning rate.
verbose (bool, optional): If ``True``, prints a message to stdout for each update. Default: ``False`` .
Returns:
``CosineAnnealingDecay`` instance to schedule learning rate.
"""
def __init__(self,
warmup_start_lr,
warmup_epochs,
cosine_base_lr,
max_epoch,
num_iters,
last_epoch=-1,
verbose=False):
self.warmup_start_lr = warmup_start_lr
self.warmup_epochs = warmup_epochs
self.cosine_base_lr = cosine_base_lr
self.max_epoch = max_epoch
self.num_iters = num_iters
#call step() in base class, last_lr/last_epoch/base_lr will be update
super(CustomWarmupCosineDecay, self).__init__(last_epoch=last_epoch,
verbose=verbose)
def step(self, epoch=None):
"""
``step`` should be called after ``optimizer.step`` . It will update the learning rate in optimizer according to current ``epoch`` .
The new learning rate will take effect on next ``optimizer.step`` .
Args:
epoch (int, None): specify current epoch. Default: None. Auto-increment from last_epoch=-1.
Returns:
None
"""
if epoch is None:
if self.last_epoch == -1:
self.last_epoch += 1
else:
self.last_epoch += 1 / self.num_iters # update step with iters
else:
self.last_epoch = epoch
self.last_lr = self.get_lr()
if self.verbose:
print('Epoch {}: {} set learning rate to {}.'.format(
self.last_epoch, self.__class__.__name__, self.last_lr))
def _lr_func_cosine(self, cur_epoch, cosine_base_lr, max_epoch):
return cosine_base_lr * (math.cos(math.pi * cur_epoch / max_epoch) +
1.0) * 0.5
def get_lr(self):
"""Define lr policy"""
lr = self._lr_func_cosine(self.last_epoch, self.cosine_base_lr,
self.max_epoch)
lr_end = self._lr_func_cosine(self.warmup_epochs, self.cosine_base_lr,
self.max_epoch)
# Perform warm up.
if self.last_epoch < self.warmup_epochs:
lr_start = self.warmup_start_lr
alpha = (lr_end - lr_start) / self.warmup_epochs
lr = self.last_epoch * alpha + lr_start
return lr
@paddle.no_grad()
def do_preciseBN(model, data_loader, parallel, num_iters=200):
"""
Recompute and update the batch norm stats to make them more precise. During
training both BN stats and the weight are changing after every iteration, so
the running average can not precisely reflect the actual stats of the
current model.
In this function, the BN stats are recomputed with fixed weights, to make
the running average more precise. Specifically, it computes the true average
of per-batch mean/variance instead of the running average.
This is useful to improve validation accuracy.
Args:
model: the model whose bn stats will be recomputed
data_loader: an iterator. Produce data as input to the model
num_iters: number of iterations to compute the stats.
Return:
the model with precise mean and variance in bn layers.
"""
bn_layers_list = [
m for m in model.sublayers()
if any((isinstance(m, bn_type)
for bn_type in (paddle.nn.BatchNorm1D, paddle.nn.BatchNorm2D,
paddle.nn.BatchNorm3D))) and m.training
]
if len(bn_layers_list) == 0:
return
# moving_mean=moving_mean*momentum+batch_mean*(1.−momentum)
# we set momentum=0. to get the true mean and variance during forward
momentum_actual = [bn._momentum for bn in bn_layers_list]
for bn in bn_layers_list:
bn._momentum = 0.
running_mean = [paddle.zeros_like(bn._mean)
for bn in bn_layers_list] #pre-ignore
running_var = [paddle.zeros_like(bn._variance) for bn in bn_layers_list]
ind = -1
for ind, data in enumerate(itertools.islice(data_loader, num_iters)):
print("doing precise BN {} / {}...".format(ind + 1, num_iters))
if parallel:
model._layers.train_step(data)
else:
model.train_step(data)
for i, bn in enumerate(bn_layers_list):
# Accumulates the bn stats.
running_mean[i] += (bn._mean - running_mean[i]) / (ind + 1)
running_var[i] += (bn._variance - running_var[i]) / (ind + 1)
assert ind == num_iters - 1, (
"update_bn_stats is meant to run for {} iterations, but the dataloader stops at {} iterations."
.format(num_iters, ind))
# Sets the precise bn stats.
for i, bn in enumerate(bn_layers_list):
bn._mean.set_value(running_mean[i])
bn._variance.set_value(running_var[i])
bn._momentum = momentum_actual[i]
def train_model(validate=True):
"""Train model entry
Args:
weights (str): weights path for finetuning.
validate (bool): Whether to do evaluation. Default: False.
"""
output_dir = f"./output/{model_name}"
if not os.path.exists(output_dir):
try:
os.makedirs(dir)
except:
pass
places = paddle.set_device('gpu')
# 1. Construct model
pptsm = ResNetTweaksTSM(pretrained=pretrained, depth=depth)
head = ppTSMHead(num_classes=num_classes,
in_channels=in_channels,
drop_ratio=drop_ratio,
std=std,
ls_eps=ls_eps)
model = Recognizer2D(backbone=pptsm, head=head)
# 2. Construct dataset and dataloader
train_pipeline = Compose(train_mode=True)
train_dataset = VideoDataset(file_path=train_file_path,
pipeline=train_pipeline,
suffix=suffix)
train_loader = build_dataloader(dataset=train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
num_workers=num_workers,
train_mode=True,
places=places,
shuffle=train_shuffle,
collate_fn_cfg=mix_collate_fn)
if validate:
valid_pipeline = Compose(train_mode=False)
valid_dataset = VideoDataset(file_path=valid_file_path,
pipeline=valid_pipeline,
suffix=suffix)
valid_loader = build_dataloader(dataset=valid_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
num_workers=num_workers,
train_mode=False,
places=places,
shuffle=valid_shuffle,
collate_fn_cfg=None)
# 3. Construct solver.
lr = CustomWarmupCosineDecay(warmup_start_lr=warmup_start_lr,
warmup_epochs=warmup_epochs,
cosine_base_lr=cosine_base_lr,
max_epoch=max_epoch,
num_iters=1)
optimizer = paddle.optimizer.Momentum(
learning_rate=lr,
momentum=momentum,
parameters=model.parameters(),
use_nesterov=True,
weight_decay=paddle.regularizer.L2Decay(coeff=1e-4))
# 4. Train Model
best = 0.
for epoch in range(0, epochs):
model.train()
record_list = build_record(framework)
tic = time.time()
for i, data in enumerate(train_loader):
record_list['reader_time'].update(time.time() - tic)
# 4.1 forward
outputs = model.train_step(data)
# 4.2 backward
avg_loss = outputs['loss']
avg_loss.backward()
# 4.3 minimize
optimizer.step()
optimizer.clear_grad()
# log record
record_list['lr'].update(optimizer.get_lr(), batch_size)
for name, value in outputs.items():
record_list[name].update(value, batch_size)
record_list['batch_time'].update(time.time() - tic)
tic = time.time()
if i % log_interval == 0:
ips = "ips: {:.5f} instance/sec.".format(
batch_size / record_list["batch_time"].val)
log_batch(record_list, i, epoch + 1, epochs, "train", ips)
# learning rate iter step
if iter_step:
lr.step()
ips = "avg_ips: {:.5f} instance/sec.".format(
batch_size * record_list["batch_time"].count /
record_list["batch_time"].sum)
log_epoch(record_list, epoch + 1, "train", ips)
def evaluate(best):
model.eval()
record_list = build_record(framework)
record_list.pop('lr')
tic = time.time()
for i, data in enumerate(valid_loader):
outputs = model.val_step(data)
# log_record
for name, value in outputs.items():
record_list[name].update(value, batch_size)
record_list['batch_time'].update(time.time() - tic)
tic = time.time()
if i % log_interval == 0:
ips = "ips: {:.5f} instance/sec.".format(
batch_size / record_list["batch_time"].val)
log_batch(record_list, i, epoch + 1, epochs, "val", ips)
ips = "avg_ips: {:.5f} instance/sec.".format(
batch_size * record_list["batch_time"].count /
record_list["batch_time"].sum)
log_epoch(record_list, epoch + 1, "val", ips)
best_flag = False
for top_flag in ['hit_at_one', 'top1']:
if record_list.get(
top_flag) and record_list[top_flag].avg > best:
best = record_list[top_flag].avg
best_flag = True
return best, best_flag
# use precise bn to improve acc
if preciseBN and (epoch % preciseBN_interval == 0 or epoch == epochs - 1):
do_preciseBN(
model, train_loader, False,
min(num_iters_preciseBN, len(train_loader)))
# 5. Validation
if validate and (epoch % val_interval == 0
or epoch == epochs - 1):
with paddle.no_grad():
best, save_best_flag = evaluate(best)
# save best
if save_best_flag:
paddle.save(optimizer.state_dict(),
osp.join(output_dir, model_name + "_best.pdopt"))
paddle.save(model.state_dict(),
osp.join(output_dir, model_name + "_best.pdparams"))
print(
f"Already save the best model (top1 acc){int(best *10000)/10000}"
)
# 6. Save model and optimizer
if epoch % save_interval == 0 or epoch == epochs - 1:
paddle.save(
optimizer.state_dict(),
osp.join(output_dir,
model_name + f"_epoch_{epoch+1:05d}.pdopt"))
paddle.save(
model.state_dict(),
osp.join(output_dir,
model_name + f"_epoch_{epoch+1:05d}.pdparams"))
print(f'training {model_name} finished')
# 在执行代码过程中,如果出现 ‘ValueError: parameter name [conv1_weights] have be been used’ 问题,
# 可以点击上方的第三个按钮 ‘重启并运行全部’ 来解决
train_model(True)
2.5 模型评估
class CenterCropMetric(object):
def __init__(self, data_size, batch_size, log_interval=20):
"""prepare for metrics
"""
super().__init__()
self.data_size = data_size
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.log_interval = log_interval
self.top1 = []
self.top5 = []
def update(self, batch_id, data, outputs):
"""update metrics during each iter
"""
labels = data[1]
top1 = paddle.metric.accuracy(input=outputs, label=labels, k=1)
top5 = paddle.metric.accuracy(input=outputs, label=labels, k=5)
self.top1.append(top1.numpy())
self.top5.append(top5.numpy())
# preds ensemble
if batch_id % self.log_interval == 0:
print("[TEST] Processing batch {}/{} ...".format(batch_id, self.data_size // self.batch_size))
def accumulate(self):
"""accumulate metrics when finished all iters.
"""
print('[TEST] finished, avg_acc1= {}, avg_acc5= {} '.format(
np.mean(np.array(self.top1)), np.mean(np.array(self.top5)))
)
def test_model(weights):
places = paddle.set_device('gpu')
# 1. Construct model
pptsm = ResNetTweaksTSM(pretrained=None, depth=depth)
head = ppTSMHead(num_classes=num_classes,
in_channels=in_channels,
drop_ratio=drop_ratio,
std=std,
ls_eps=ls_eps)
model = Recognizer2D(backbone=pptsm, head=head)
# 2. Construct dataset and dataloader
test_pipeline = Compose(train_mode=False)
test_dataset = VideoDataset(file_path=valid_file_path,
pipeline=test_pipeline,
suffix=suffix)
test_sampler = paddle.io.DistributedBatchSampler(test_dataset,
batch_size=test_batch_size,
shuffle=valid_shuffle,
drop_last=False)
test_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(test_dataset,
batch_sampler=test_sampler,
places=places,
return_list=True)
model.eval()
state_dicts = paddle.load(weights)
model.set_state_dict(state_dicts)
# add params to metrics
data_size = len(test_dataset)
metric = CenterCropMetric(data_size=data_size, batch_size=test_batch_size)
for batch_id, data in enumerate(test_loader):
outputs = model.test_step(data)
metric.update(batch_id, data, outputs)
metric.accumulate()
# 在执行代码过程中,如果出现 ‘ValueError: parameter name [conv1_weights] have be been used’ 问题,
# 可以点击上方的第三个按钮 ‘重启并运行全部’ 来解决
model_file = './output/ppTSM/ppTSM_best.pdparams'
test_model(model_file)
2.6 模型推理
def inference():
model_file = './output/ppTSM/ppTSM_best.pdparams'
# 1. Construct model
pptsm = ResNetTweaksTSM(pretrained=None, depth=depth)
head = ppTSMHead(num_classes=num_classes,
in_channels=in_channels,
drop_ratio=drop_ratio,
std=std,
ls_eps=ls_eps)
model = Recognizer2D(backbone=pptsm, head=head)
# 2. Construct dataset and dataloader
test_pipeline = Compose(train_mode=False)
test_dataset = VideoDataset(file_path=valid_file_path,
pipeline=test_pipeline,
suffix=suffix)
test_sampler = paddle.io.DistributedBatchSampler(test_dataset,
batch_size=10,
shuffle=True,
drop_last=False)
test_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(test_dataset,
batch_sampler=test_sampler,
places=paddle.set_device('gpu'),
return_list=True)
model.eval()
state_dicts = paddle.load(model_file)
model.set_state_dict(state_dicts)
for batch_id, data in enumerate(test_loader):
labels = data[1]
outputs = model.test_step(data)
scores = F.softmax(outputs)
class_id = paddle.argmax(scores, axis=-1)
pred = class_id.numpy()[0]
label = labels.numpy()[0][0]
print('真实类别:{}, 模型预测类别:{}'.format(pred, label))
if batch_id > 5:
break
# 启动推理
# 在执行代码过程中,如果出现 ‘ValueError: parameter name [conv1_weights] have be been used’ 问题,
# 可以点击上方的第三个按钮 ‘重启并运行全部’ 来解决
inference()
W0112 14:03:17.916324 6956 device_context.cc:447] Please NOTE: device: 0, GPU Compute Capability: 7.0, Driver API Version: 10.1, Runtime API Version: 10.1
W0112 14:03:17.920886 6956 device_context.cc:465] device: 0, cuDNN Version: 7.6.
真实类别:14, 模型预测类别:14
真实类别:12, 模型预测类别:12
真实类别:19, 模型预测类别:19
真实类别:96, 模型预测类别:96
真实类别:90, 模型预测类别:90
真实类别:11, 模型预测类别:11
真实类别:64, 模型预测类别:64
3. 实验总结
本章提供了一个基于百度 AIStudio 平台实现的视频分类实验。本章对案例做了详尽的剖析,阐明了整个实验功能、结构与流程的设计,详细解释了如何处理数据、构建视频分类模型以及训练模型。训练好的模型在多条数据上进行测试,结果表明模型具有较快的推断速度和较好的分类性能。读者可以在该案例的基础上开发更有针对性的应用案例。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1436条内容
已为社区贡献1436条内容









所有评论(0)