数字乡桥—乡桥桥梁安全检测系统
2022中国高校计算机大赛-人工智能创意赛 参赛团队:南山之巅 天外飞仙 参赛项目:数字乡桥—乡桥桥梁安全检测系统
数字乡桥—乡桥桥梁安全检测系统
一、项目背景
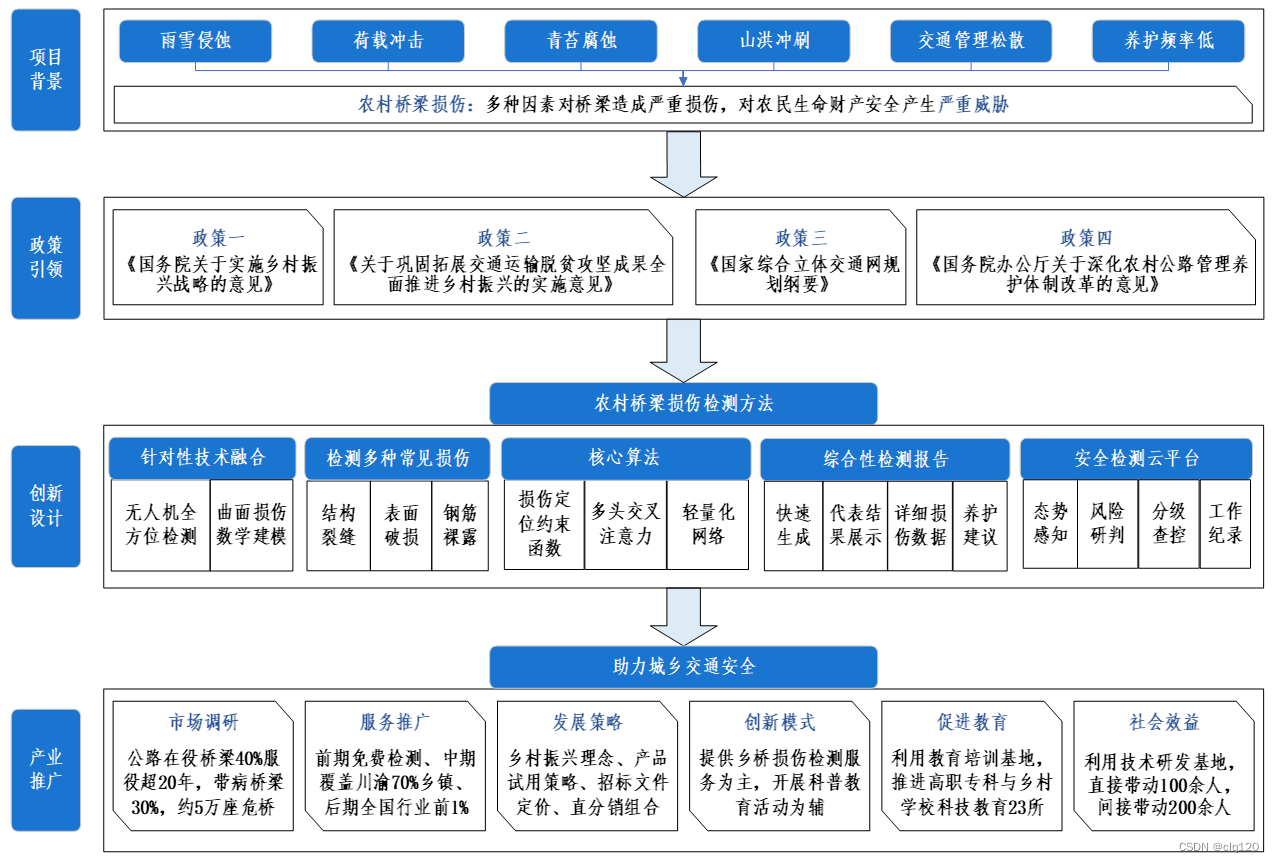
乡村振兴,交通先行。2015年以来,中央出台了《国务院关于实施乡村振兴战略的意见》、《国家综合立体交通网规划纲要》、《关于巩固拓展交通运输脱贫攻坚成果全面推进乡村振兴的实施意见》、《国务院办公厅关于深化农村公路管理养护体制改革的意见》等政策方针,进一步推动乡村振兴。其中,农村桥梁在乡村振兴中扮演了重要的角色。然而,农村桥梁常年来受到荷载冲击、山洪冲刷、雨雪侵蚀,为乡村通行埋下安全隐患,严重影响农村人民的生命财产安全。国家对此高度重视,2021和2022年出台的两份中央一号文件中明确指出,要加强农村公路桥梁安全隐患排查和稳步推进农村公路路况自动化检测。
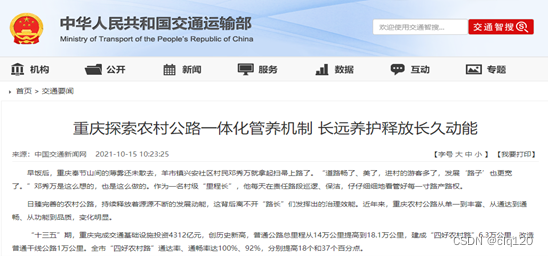
“桥都”重庆是我国唯一具有大农村、大山区特点的都市,全市共有超过1500万农村人口,乡村道路桥梁运输承载着乡村人民的致富梦想、振兴希望。重庆市“十四五”规划中也明确提出要加强农村道路桥梁安全隐患排查力度。
二、研究目的
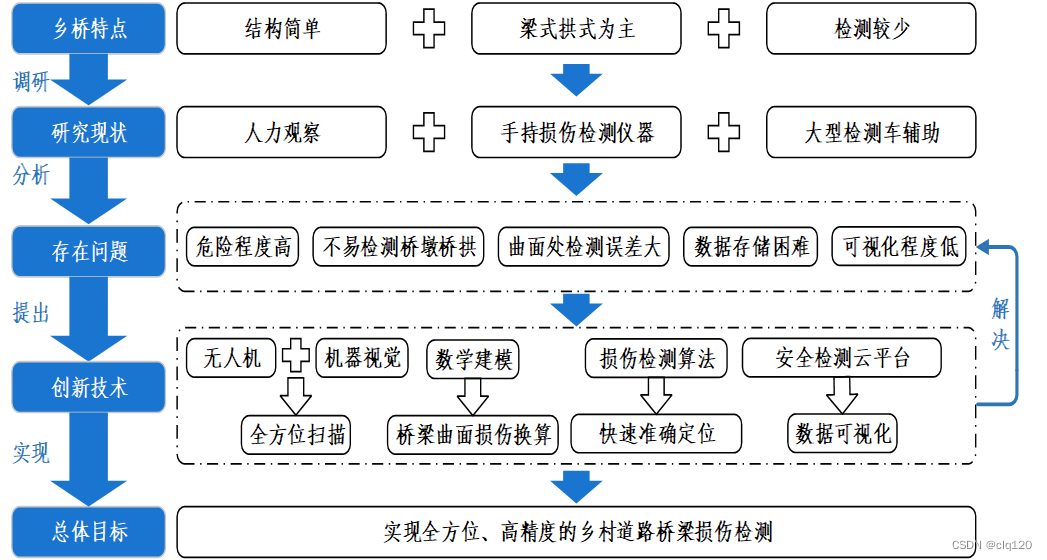
本团队成员立足于城乡交通的安全问题,紧随国家交通安全隐患排查政策,针对农村道路桥梁使用时间久,检测维护较少的问题,设计了一种基于无人机结合机器视觉、物联网、深度学习等新兴技术的乡村道路桥梁损伤检测系统。该系统针对乡村桥梁多为梁氏、拱式的特点,利用无人机搭载的“N”字形激光阵列对桥梁曲面处进行损伤测量,针对桥梁损伤特征设计的AI算法能够快速、精准的识别各类损伤,使用大数据分析的手段快速给出检测报告和诊断报告,以及利用大数据云平台实现各类损伤数据的可视化。该技术方案经过科技查新认证,处于行业领先地位(附录六)。检测系统有效地提高了道路桥梁的检测效率,使得城乡交通道路桥梁的检测和养护更加智能化,信息化。未来,该项目成果可广泛应用于全国城乡交通桥梁的安全监测,具有广阔的市场前景。
三、行业调研
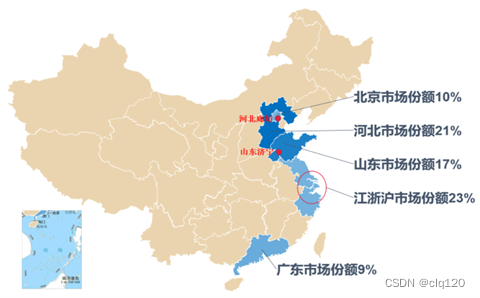
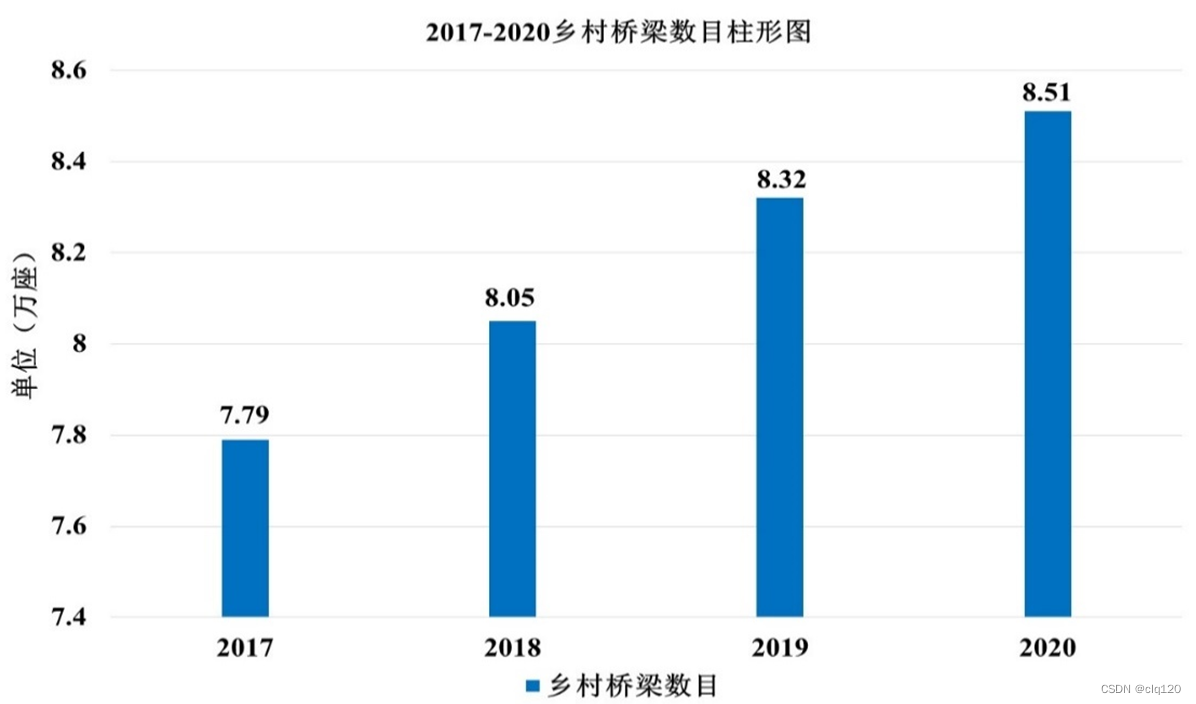
我国道路、桥梁安全检测仪器的生产企业主要集中分布在山东济宁、河北廊坊,以及经济技术较为发达的地区,如北京、上海、江苏等省份。现阶段大多数公司设计的道路损伤检测仪器主要针对城市的道路桥梁。然而,全面建设社会主义现代化国家,实现中华民族伟大复兴,最艰巨最繁重的任务依然在农村,最广泛最深厚的基础依然在农村。农村桥梁作为城乡交通的重要设施,在人民的日常生活、出行以及乡村经济发展中有着不可替代的重要作用。
四、作品内容
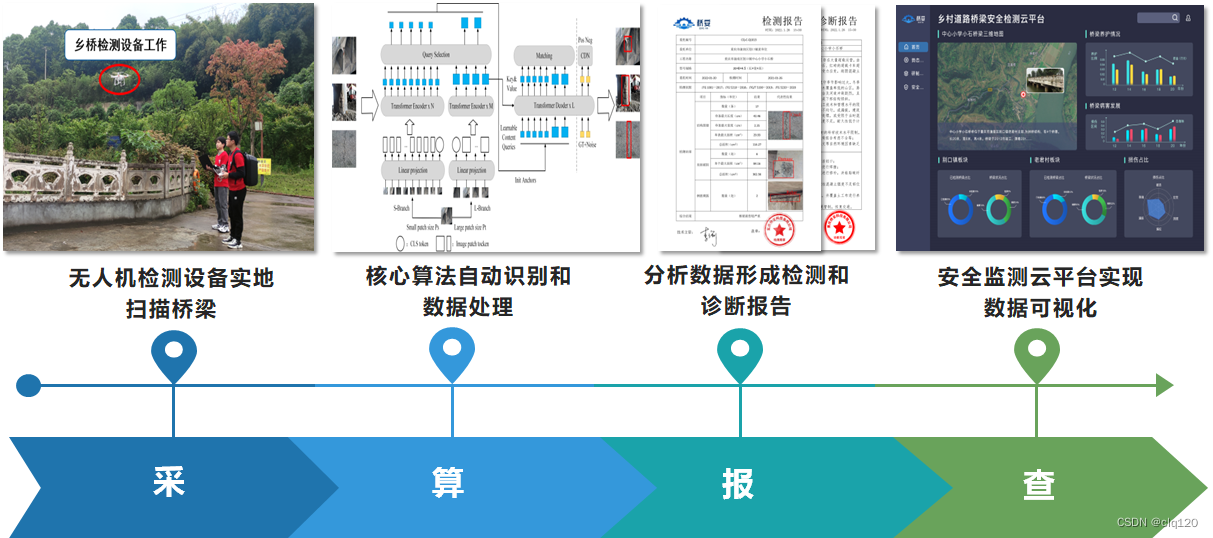
针对乡村道路桥梁交通管制松散、自然因素破坏、施工不精细等现实问题,我们依托于自主研发的 “一种基于激光阵列辅助机器视觉的桥梁损伤测量方法”、“基于自适应多特征融合的小目标检测方法”、“一种引入注意力机制改进型U-net的混凝土裂缝实时检测方法”等10余项专利技术,设计了“采—算—报—查”一体化的乡村道路桥梁检测系统,为乡村提供“安全可靠,即检即查”的智能化桥梁检测服务。该技术方案经过科技查新认证,处于行业领先地位。
团队大力响应2021年中央一号文件关于“加强农村道路桥梁安全隐患排查”的要求,在项目初期,我们对川渝地区的85座乡村桥梁进行了损伤检测与安全评估,得到了部分村委会的衷心感谢,并将检测结果交于当地相关政府部门,获得了重庆市永川区、潼南区、四川省阆中市乡村振兴局、公路管理养护局等政府部门的高度认可与大力推荐。同时获得了今日头条、搜狐新闻、腾讯新闻等多家主流新闻媒体的专题报道,并与润达公路工程有限公司、重庆亚派桥梁工程质量检测有限公司、重庆现代建筑产业发展研究院等建立合作关系。我们旨在通过使用新兴技术贯彻落实国家“十四五”规划和“乡村振兴”战略,巩固拓展交通运输脱贫攻坚成果,为广大农民脱贫致富提供保障。
请点击此处查看本环境基本用法.
Please click here for more detailed instructions.
五、创新点
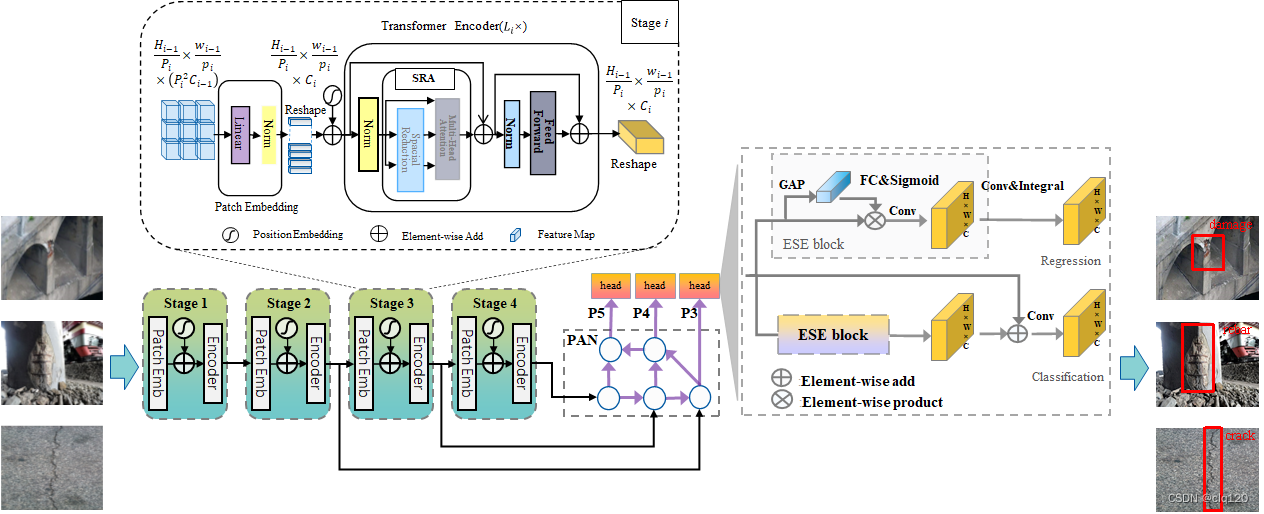
1、Damage-former核心算法进行损伤检测
为了更准确的进行桥梁健康监测,在使用无人机携带嵌入式AI设备进行桥梁损伤检测时,需要提高嵌入式AI设备运行的传统目标检测算法的准确度。考虑无人机在进行实际检测时,距离桥墩、桥侧以及裸露的钢筋要保持一定的距离,在实际使用时对于一些损伤常常存在漏检,为了尽可能的减少漏检,我们采用Backbone+neck+head结构,使用PVTv2作为backbone,在neck部分使用多尺度的融合并使用注意力模块的解耦头。在实际测试中,准确率达到了95%,同时网络参数只有18M,检测速度达到了40FPS。
###############################################################
backbone:
class PvTv2Block(nn.Layer):
"""Pyramid VisionTransformerV2 block
Contains multi head efficient self attention, droppath, mlp, norm.
Attributes:
dim: int, input dimension (channels)
num_heads: int, number of attention heads
mlp_ratio: float, ratio of mlp hidden dim and input embedding dim, default: 4.
sr_ratio: the spatial reduction ratio of SRA (linear spatial reduction attention)
qkv_bias: bool, if True, enable learnable bias to q,k,v, default: True
qk_scale: float, override default qk scale head_dim**-0.5 if set, default: None
dropout: float, dropout for output, default: 0.
attention_dropout: float, dropout of attention, default: 0.
drop_path: float, drop path rate, default: 0.
"""
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads, mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=False, qk_scale=None, dropout=0.,
attention_dropout=0., drop_path=0., sr_ratio=1, linear=False):
super(PvTv2Block, self).__init__()
self.norm1 = nn.LayerNorm(dim, epsilon=1e-6)
self.attn = Attention(dim,
num_heads=num_heads,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias,
qk_scale=qk_scale,
attention_dropout=attention_dropout,
dropout=dropout,
sr_ratio=sr_ratio,
linear=linear)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else Identity()
self.norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(dim, epsilon=1e-6)
self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=int(dim*mlp_ratio), dropout=dropout, linear=linear)
def _init_weights(self):
weight_attr = paddle.ParamAttr(initializer=nn.initializer.KaimingUniform())
bias_attr = paddle.ParamAttr(initializer=nn.initializer.KaimingUniform())
return weight_attr, bias_attr
def forward(self, x, H, W):
x = x + self.drop_path(self.attn(self.norm1(x), H, W))
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x), H, W))
return x
class PyramidVisionTransformerV2(nn.Layer):
"""PyramidVisionTransformerV2 class
Attributes:
patch_size: int, size of patch
image_size: int, size of image
num_classes: int, num of image classes
in_channels: int, channel of input image
num_heads: int, num of heads in attention module
num_stages: int, num of stages contains OverlapPatch embedding and PvTv2 blocks
depths: list of int, num of PvTv2 blocks in each stage
mlp_ratio: float, hidden dimension of mlp layer is mlp_ratio * mlp input dim
sr_ratio: the spatial reduction ratio of SRA (linear spatial reduction attention)
qkv_bias: bool, if True, set qkv layers have bias enabled
qk_scale: float, scale factor for qk.
embed_dims: list of int, output dimension of patch embedding
dropout: float, dropout rate for linear layer
attention_dropout: float, dropout rate for attention
drop_path: float, drop path rate, default: 0.
linear: bool, if True, use linear spatial reduction attention instead of spatial reduction attention
patch_embedding: PatchEmbedding, patch embedding instance
norm: nn.LayerNorm, norm layer applied after transformer
fc: nn.Linear, classifier op.
"""
def __init__(self,
image_size=224,
patch_size=4,
embed_dims=[32, 64, 160, 256],
in_channels=3,
num_heads=[1, 2, 5, 8],
depths=[2, 2, 2, 2],
mlp_ratio=[8, 8, 4, 4],
sr_ratio=[8, 4, 2, 1],
qkv_bias=True,
qk_scale=None,
dropout=0.,
attention_dropout=0.,
drop_path=0.,
return_idx=[1, 2, 3],
linear=False,
pretrained=None):
super(PyramidVisionTransformerV2, self).__init__()
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.image_size = image_size
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.depths = depths
self.num_stages = len(self.depths)
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
self.sr_ratio = sr_ratio
self.qkv_bias = qkv_bias
self.qk_scale = qk_scale
self.embed_dims = embed_dims
self.dropout = dropout
self.attention_dropout = attention_dropout
self.drop_path = drop_path
self.linear = linear
depth_decay = [x.item() for x in paddle.linspace(0, self.drop_path, sum(self.depths))]
cur = 0
for i in range(self.num_stages):
patch_embedding = OverlapPatchEmbedding(image_size=self.image_size if i == 0 else self.image_size // (2 ** (i + 1)),
patch_size=7 if i == 0 else 3,
stride=4 if i == 0 else 2,
in_channels=self.in_channels if i == 0 else self.embed_dims[i - 1],
embed_dim=self.embed_dims[i])
block = nn.LayerList([copy.deepcopy(PvTv2Block(
dim=self.embed_dims[i], num_heads=self.num_heads[i], mlp_ratio=self.mlp_ratio[i], qkv_bias=self.qkv_bias,
qk_scale=self.qk_scale, dropout=self.dropout, attention_dropout=self.attention_dropout,
drop_path=depth_decay[cur + j], sr_ratio=self.sr_ratio[i], linear=self.linear))
for j in range(self.depths[i])])
norm = nn.LayerNorm(self.embed_dims[i], epsilon=1e-6)
cur += self.depths[i]
setattr(self, f"patch_embedding{i + 1}", patch_embedding)
setattr(self, f"block{i + 1}", block)
setattr(self, f"norm{i + 1}", norm)
self.out_channels = self.embed_dims[1:]
# 输出的步长stride[4,8,16,32]
self._out_strides = [4 * 2 ** i for i in range(len(self.depths))]
self.return_idx = return_idx
self.init_weights(pretrained)
def _init_weights(self):
weight_attr = paddle.ParamAttr(initializer=nn.initializer.KaimingUniform())
bias_attr = paddle.ParamAttr(initializer=nn.initializer.KaimingUniform())
return weight_attr, bias_attr
def init_weights(self, pretrained=None):
if isinstance(pretrained, str):
model_state_dict = paddle.load(pretrained)
self.set_state_dict(model_state_dict)
def freeze_patch_embedding(self):
self.patch_embedding1.requires_grad = False
def forward(self, inputs):
x = inputs['image']
B = x.shape[0]
outs = []
for i in range(self.num_stages):
patch_embedding = getattr(self, f"patch_embedding{i + 1}")
block = getattr(self, f"block{i + 1}")
norm = getattr(self, f"norm{i + 1}")
x, H, W = patch_embedding(x)
for idx, blk in enumerate(block):
x = blk(x, H, W)
x = norm(x)
x = x.reshape([B, H, W, -1]).transpose([0, 3, 1, 2])
if i in self.return_idx:
outs.append(x)
return outs
@property
def out_shape(self):
return [
ShapeSpec(channels=self.out_channels[i], stride=self._out_strides[i])
for i in self.return_idx
]
##############################################################
neck:
import paddle
import paddle.nn as nn
import paddle.nn.functional as F
from paddle import ParamAttr
__all__ = ['CSPPAN']
class ConvBNLayer(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, in_channel=96, out_channel=96, kernel_size=3, stride=1, groups=1, act='leaky_relu'):
super(ConvBNLayer, self).__init__()
initializer = nn.initializer.KaimingUniform()
self.conv = nn.Conv2D(
in_channels=in_channel,
out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
groups=groups,
padding=(kernel_size - 1) // 2,
stride=stride,
weight_attr=ParamAttr(initializer=initializer),
bias_attr=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2D(out_channel)
if act == "hard_swish":
act = 'hardswish'
self.act = act
def forward(self, x):
x = self.bn(self.conv(x))
if self.act:
x = getattr(F, self.act)(x)
return x
class DPModule(nn.Layer):
"""
Depth-wise and point-wise module.
Args:
in_channel (int): The input channels of this Module.
out_channel (int): The output channels of this Module.
kernel_size (int): The conv2d kernel size of this Module.
stride (int): The conv2d's stride of this Module.
act (str): The activation function of this Module,
Now support `leaky_relu` and `hard_swish`.
"""
def __init__(self, in_channel=96, out_channel=96, kernel_size=3, stride=1, act='leaky_relu', use_act_in_out=True):
super(DPModule, self).__init__()
initializer = nn.initializer.KaimingUniform()
self.use_act_in_out = use_act_in_out
self.dwconv = nn.Conv2D(
in_channels=in_channel,
out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
groups=out_channel,
padding=(kernel_size - 1) // 2,
stride=stride,
weight_attr=ParamAttr(initializer=initializer),
bias_attr=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2D(out_channel)
self.pwconv = nn.Conv2D(
in_channels=out_channel,
out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=1,
groups=1,
padding=0,
weight_attr=ParamAttr(initializer=initializer),
bias_attr=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2D(out_channel)
if act == "hard_swish":
act = 'hardswish'
self.act = act
def forward(self, x):
x = self.bn1(self.dwconv(x))
if self.act:
x = getattr(F, self.act)(x)
x = self.bn2(self.pwconv(x))
if self.use_act_in_out and self.act:
x = getattr(F, self.act)(x)
return x
class DarknetBottleneck(nn.Layer):
"""The basic bottleneck block used in Darknet.
Each Block consists of two ConvModules and the input is added to the
final output. Each ConvModule is composed of Conv, BN, and act.
The first convLayer has filter size of 1x1 and the second one has the
filter size of 3x3.
Args:
in_channels (int): The input channels of this Module.
out_channels (int): The output channels of this Module.
expansion (int): The kernel size of the convolution. Default: 0.5
add_identity (bool): Whether to add identity to the out.
Default: True
use_depthwise (bool): Whether to use depthwise separable convolution.
Default: False
"""
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size=3,
expansion=0.5,
add_identity=True,
use_depthwise=False,
act="leaky_relu"):
super(DarknetBottleneck, self).__init__()
hidden_channels = int(out_channels * expansion)
conv_func = DPModule if use_depthwise else ConvBNLayer
self.conv1 = ConvBNLayer(
in_channel=in_channels,
out_channel=hidden_channels,
kernel_size=1,
act=act)
self.conv2 = conv_func(
in_channel=hidden_channels,
out_channel=out_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=1,
act=act)
self.add_identity = \
add_identity and in_channels == out_channels
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.conv2(out)
if self.add_identity:
return out + identity
else:
return out
class CSPLayer(nn.Layer):
"""Cross Stage Partial Layer.
Args:
in_channels (int): The input channels of the CSP layer.
out_channels (int): The output channels of the CSP layer.
expand_ratio (float): Ratio to adjust the number of channels of the
hidden layer. Default: 0.5
num_blocks (int): Number of blocks. Default: 1
add_identity (bool): Whether to add identity in blocks.
Default: True
use_depthwise (bool): Whether to depthwise separable convolution in
blocks. Default: False
"""
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size=3,
expand_ratio=0.5,
num_blocks=1,
add_identity=True,
use_depthwise=False,
act="leaky_relu"):
super().__init__()
mid_channels = int(out_channels * expand_ratio)
self.main_conv = ConvBNLayer(in_channels, mid_channels, 1, act=act)
self.short_conv = ConvBNLayer(in_channels, mid_channels, 1, act=act)
self.final_conv = ConvBNLayer(
2 * mid_channels, out_channels, 1, act=act)
self.blocks = nn.Sequential(* [
DarknetBottleneck(
mid_channels,
mid_channels,
kernel_size,
1.0,
add_identity,
use_depthwise,
act=act) for _ in range(num_blocks)
])
def forward(self, x):
x_short = self.short_conv(x)
x_main = self.main_conv(x)
x_main = self.blocks(x_main)
x_final = paddle.concat((x_main, x_short), axis=1)
return self.final_conv(x_final)
class Channel_T(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, in_channels=[116, 232, 464], out_channels=96, act="leaky_relu"):
super(Channel_T, self).__init__()
self.convs = nn.LayerList()
for i in range(len(in_channels)):
self.convs.append(ConvBNLayer(in_channels[i], out_channels, 1, act=act))
def forward(self, x):
outs = [self.convs[i](x[i]) for i in range(len(x))]
return outs
# Path Aggregation Network with CSP module
class CSPPAN(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size=5,
num_features=3,
num_csp_blocks=1,
use_depthwise=True,
act='hard_swish',
spatial_scales=[0.125, 0.0625, 0.03125]):
super(CSPPAN, self).__init__()
# 特征整合,三个输入通道数固定为out_channels
self.conv_t = Channel_T(in_channels, out_channels, act=act)
in_channels = [out_channels] * len(spatial_scales)
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = [out_channels] * len(spatial_scales)
self.spatial_scales = spatial_scales
self.num_features = num_features
conv_func = DPModule if use_depthwise else ConvBNLayer
if self.num_features == 4:
self.first_top_conv = conv_func(
in_channels[0], in_channels[0], kernel_size, stride=2, act=act)
self.second_top_conv = conv_func(
in_channels[0], in_channels[0], kernel_size, stride=2, act=act)
self.spatial_scales.append(self.spatial_scales[-1] / 2)
# 自上而下top-down blocks
self.upsample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
self.top_down_blocks = nn.LayerList()
for idx in range(len(in_channels)-1, 0, -1):
self.top_down_blocks.append(
CSPLayer(
in_channels[idx-1] * 2,
in_channels[idx-1],
kernel_size=kernel_size,
num_blocks=num_csp_blocks,
add_identity=False,
use_depthwise=use_depthwise,
act=act))
# 自下而上bottom-up blocks
self.downsamples = nn.LayerList()
self.bottom_up_blocks = nn.LayerList()
for idx in range(len(in_channels) - 1):
self.downsamples.append(
conv_func(
in_channels[idx],
in_channels[idx],
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=2,
act=act))
self.bottom_up_blocks.append(
CSPLayer(
in_channels[idx] * 2,
in_channels[idx+1],
kernel_size=kernel_size,
num_blocks=num_csp_blocks,
add_identity=False,
use_depthwise=use_depthwise,
act=act))
def forward(self, inputs):
# inputs
# [4, 128, 80, 80] 1/8 小目标
# [4, 320, 40, 40] 1/16 中目标
# [4, 512, 20, 20] 1/32 大目标
assert len(inputs) == len(self.in_channels)
inputs = self.conv_t(inputs)
# top-down path
inner_outs = [inputs[-1]]
for idx in range(len(self.in_channels)-1, 0, -1):
feat_heigh = inner_outs[0]
feat_low = inputs[idx-1]
upsample_feat = self.upsample(feat_heigh)
inner_out = self.top_down_blocks[len(self.in_channels) - 1 - idx](
paddle.concat([upsample_feat, feat_low], 1))
inner_outs.insert(0, inner_out)
# bottom-up path
outs = [inner_outs[0]]
for idx in range(len(self.in_channels) - 1):
feat_low = outs[-1]
feat_height = inner_outs[idx + 1]
downsample_feat = self.downsamples[idx](feat_low)
out = self.bottom_up_blocks[idx](paddle.concat(
[downsample_feat, feat_height], 1))
outs.append(out)
top_features = None
if self.num_features == 4:
top_features = self.first_top_conv(inputs[-1])
top_features = top_features + self.second_top_conv(outs[-1])
outs.append(top_features)
# print(outs[0].shape)
# print(outs[1].shape)
# print(outs[2].shape)
return tuple(outs)
###############################################################
head:
class PPYOLOEHead(nn.Layer):
__shared__ = ['num_classes', 'eval_size', 'trt', 'exclude_nms']
__inject__ = ['static_assigner', 'assigner', 'nms']
def __init__(self,
in_channels=[1024, 512, 256],
num_classes=80,
act='swish',
fpn_strides=(32, 16, 8),
grid_cell_scale=5.0,
grid_cell_offset=0.5,
reg_max=16,
static_assigner_epoch=5,
use_varifocal_loss=True,
eval_size=None,
loss_weight=None,
trt=False,
exclude_nms=False):
super(PPYOLOEHead, self).__init__()
if loss_weight is None:
loss_weight = {
'class': 1.0,
'iou': 2.5,
'dfl': 0.5,
}
assert len(in_channels) > 0, "len(in_channels) should > 0"
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.fpn_strides = fpn_strides
self.grid_cell_scale = grid_cell_scale
self.grid_cell_offset = grid_cell_offset
self.reg_max = reg_max
self.iou_loss = GIoULoss()
self.loss_weight = loss_weight
self.use_varifocal_loss = use_varifocal_loss
self.eval_size = eval_size
self.static_assigner_epoch = static_assigner_epoch
# 静态正负样本匹配器
self.static_assigner = ATSSAssigner(num_classes=num_classes)
# 动态正负样本匹配器
self.assigner = TaskAlignedAssigner()
self.nms = MultiClassNMS()
if isinstance(self.nms, MultiClassNMS) and trt:
self.nms.trt = trt
self.exclude_nms = exclude_nms
# stem卷积
self.stem_cls = nn.LayerList()
self.stem_reg = nn.LayerList()
act = get_act_fn(act, trt=trt) if act is None or isinstance(act, (str, dict)) else act
for in_c in self.in_channels:
self.stem_cls.append(ESEAttn(in_c, act=act))
self.stem_reg.append(ESEAttn(in_c, act=act))
# pred_head卷积
self.pred_cls = nn.LayerList()
self.pred_reg = nn.LayerList()
for in_c in self.in_channels:
self.pred_cls.append(nn.Conv2D(in_c, self.num_classes, 3, padding=1))
self.pred_reg.append(nn.Conv2D(in_c, 4*(self.reg_max+1), 3, padding=1))
# projection conv
self.proj_conv = nn.Conv2D(self.reg_max+1, 1, 1, bias_attr=False)
self._init_weights()
def _init_weights(self):
bias_cls = bias_init_with_prob(0.01)
for cls_, reg_ in zip(self.pred_cls, self.pred_reg):
constant_(cls_.weight)
constant_(cls_.bias, bias_cls)
constant_(reg_.weight)
constant_(reg_.bias, 1.0)
self.proj = paddle.linspace(0, self.reg_max, self.reg_max+1)
self.proj_conv.weight.set_value(self.proj.reshape([1, self.reg_max+1, 1, 1]))
self.proj_conv.weight.stop_gradient = True
if self.eval_size:
anchor_points, stride_tensor = self._generate_anchors()
self.anchor_points = anchor_points
self.stride_tensor = stride_tensor
def forward_train(self, feats, targets):
# feats: 列表,[8, 1024, 20, 20] [8, 512, 40, 40] [8, 256, 80, 80]
# targets: 字典,['im_id', 'is_crowd', 'gt_class', 'gt_bbox', 'curr_iter',
# 'image', 'im_shape', 'scale_factor', 'pad_gt_mask', 'epoch_id']
anchors, anchor_points, num_anchors_list, stride_tensor = \
generate_anchors_for_grid_cell(feats, self.fpn_strides, self.grid_cell_scale, self.grid_cell_offset)
cls_score_list = []
reg_distri_list = []
# 对于每个尺度的特征图feature来说
# [bs, num_classes, 20, 20], [bs, 4*reg_max, 20, 20]
# [bs, num_classes, 40, 40], [bs, 4*reg_max, 40, 40]
# [bs, num_classes, 80, 80], [bs, 4*reg_max, 80, 80]
for i, feat in enumerate(feats):
avg_feat = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(feat, (1, 1))
# 分类头 class_head
cls_logit = self.pred_cls[i](self.stem_cls[i](feat, avg_feat) + feat)
# 回归头 reg_head
reg_distri = self.pred_reg[i](self.stem_reg[i](feat, avg_feat))
cls_score = F.sigmoid(cls_logit)
cls_score_list.append(cls_score.flatten(2).transpose([0, 2, 1]))
reg_distri_list.append(reg_distri.flatten(2).transpose([0, 2, 1]))
cls_score_list = paddle.concat(cls_score_list, axis=1)
reg_distri_list = paddle.concat(reg_distri_list, axis=1)
return self.get_loss([
cls_score_list, reg_distri_list, anchors, anchor_points,
num_anchors_list, stride_tensor
], targets)
def _generate_anchors(self, feats=None):
# just use in eval time
anchor_points = []
stride_tensor = []
for i, stride in enumerate(self.fpn_strides):
if feats is not None:
_, _, h, w = feats[i].shape
else:
h = int(self.eval_size[0] / stride)
w = int(self.eval_size[1] / stride)
shift_x = paddle.arange(end=w) + self.grid_cell_offset
shift_y = paddle.arange(end=h) + self.grid_cell_offset
shift_y, shift_x = paddle.meshgrid(shift_y, shift_x)
anchor_point = paddle.cast(paddle.stack([shift_x, shift_y], axis=-1), dtype='float32')
anchor_points.append(anchor_point.reshape([-1, 2]))
stride_tensor.append(paddle.full([h * w, 1], stride, dtype='float32'))
anchor_points = paddle.concat(anchor_points)
stride_tensor = paddle.concat(stride_tensor)
return anchor_points, stride_tensor
def forward_eval(self, feats):
if self.eval_size:
anchor_points, stride_tensor = self.anchor_points, self.stride_tensor
else:
anchor_points, stride_tensor = self._generate_anchors(feats)
cls_score_list, reg_dist_list = [], []
# 对于每个尺度的特征图feature来说
# [bs, num_classes, 20, 20], [bs, 4*reg_max, 20, 20]
# [bs, num_classes, 40, 40], [bs, 4*reg_max, 40, 40]
# [bs, num_classes, 80, 80], [bs, 4*reg_max, 80, 80]
for i, feat in enumerate(feats):
b, _, h, w = feat.shape
l = h * w
avg_feat = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(feat, (1, 1))
# 分类头 class_head
cls_logit = self.pred_cls[i](self.stem_cls[i](feat, avg_feat) + feat)
# 回归头 reg_head
reg_dist = self.pred_reg[i](self.stem_reg[i](feat, avg_feat))
# (bs, reg_max+1, 4, l)
reg_dist = reg_dist.reshape([-1, 4, self.reg_max+1, l]).transpose([0, 2, 1, 3])
reg_dist = self.proj_conv(F.softmax(reg_dist, axis=1))
cls_score = F.sigmoid(cls_logit)
cls_score_list.append(cls_score.reshape([b, self.num_classes, l]))
reg_dist_list.append(reg_dist.reshape([b, 4, l]))
cls_score_list = paddle.concat(cls_score_list, axis=-1)
reg_dist_list = paddle.concat(reg_dist_list, axis=-1)
return cls_score_list, reg_dist_list, anchor_points, stride_tensor
def forward(self, feats, targets=None):
assert len(feats) == len(self.fpn_strides), "The size of feats is not equal to size of fpn_strides"
# 训练
if self.training:
return self.forward_train(feats, targets)
# 验证/测试
else:
return self.forward_eval(feats)
@staticmethod
def _focal_loss(score, label, alpha=0.25, gamma=2.0):
weight = (score - label).pow(gamma)
if alpha > 0:
alpha_t = alpha * label + (1 - alpha) * (1 - label)
weight *= alpha_t
loss = F.binary_cross_entropy(score, label, weight=weight, reduction='sum')
return loss
@staticmethod
# https://blog.csdn.net/calvinpaean/article/details/115497134
def _varifocal_loss(pred_score, gt_score, label, alpha=0.75, gamma=2.0):
weight = alpha * pred_score.pow(gamma) * (1 - label) + gt_score * label
loss = F.binary_cross_entropy(pred_score, gt_score, weight=weight, reduction='sum')
return loss
def _bbox_decode(self, anchor_points, pred_dist):
b, l, _ = get_static_shape(pred_dist)
# (b, l, 4, reg_max+1)--->(b, l, 4)
pred_dist = F.softmax(pred_dist.reshape([b, l, 4, self.reg_max+1])).matmul(self.proj)
return batch_distance2bbox(anchor_points, pred_dist)
def _bbox2distance(self, points, bbox):
x1y1, x2y2 = paddle.split(bbox, 2, -1)
lt = points - x1y1
rb = x2y2 - points
return paddle.concat([lt, rb], -1).clip(0, self.reg_max - 0.01)
def _df_loss(self, pred_dist, target):
target_left = paddle.cast(target, 'int64')
target_right = target_left + 1
weight_left = target_right.astype('float32') - target
weight_right = 1 - weight_left
loss_left = F.cross_entropy(pred_dist, target_left, reduction='none') * weight_left
loss_right = F.cross_entropy(pred_dist, target_right, reduction='none') * weight_right
return (loss_left + loss_right).mean(-1, keepdim=True)
def _bbox_loss(self, pred_dist, pred_bboxes, anchor_points, assigned_labels,
assigned_bboxes, assigned_scores, assigned_scores_sum):
# select positive samples mask
mask_positive = (assigned_labels != self.num_classes)
num_pos = mask_positive.sum()
# pos/neg loss
if num_pos > 0:
# l1 + iou
bbox_mask = mask_positive.unsqueeze(-1).tile([1, 1, 4])
pred_bboxes_pos = paddle.masked_select(pred_bboxes, bbox_mask).reshape([-1, 4])
assigned_bboxes_pos = paddle.masked_select(assigned_bboxes, bbox_mask).reshape([-1, 4])
bbox_weight = paddle.masked_select(assigned_scores.sum(-1), mask_positive).unsqueeze(-1)
loss_l1 = F.l1_loss(pred_bboxes_pos, assigned_bboxes_pos)
loss_iou = self.iou_loss(pred_bboxes_pos, assigned_bboxes_pos) * bbox_weight
loss_iou = loss_iou.sum() / assigned_scores_sum
dist_mask = mask_positive.unsqueeze(-1).tile([1, 1, (self.reg_max + 1) * 4])
pred_dist_pos = paddle.masked_select(pred_dist, dist_mask).reshape([-1, 4, self.reg_max + 1])
assigned_ltrb = self._bbox2distance(anchor_points, assigned_bboxes)
assigned_ltrb_pos = paddle.masked_select(assigned_ltrb, bbox_mask).reshape([-1, 4])
loss_dfl = self._df_loss(pred_dist_pos, assigned_ltrb_pos) * bbox_weight
loss_dfl = loss_dfl.sum() / assigned_scores_sum
else:
loss_l1 = paddle.zeros([1])
loss_iou = paddle.zeros([1])
loss_dfl = pred_dist.sum() * 0.
return loss_l1, loss_iou, loss_dfl
def get_loss(self, head_outs, gt_meta):
# pred_scores(bs, n_anchors, num_classes)
pred_scores, pred_distri, anchors, anchor_points, num_anchors_list, stride_tensor = head_outs
# 将anchor points大小放缩为当前特征图大小
anchor_points_s = anchor_points / stride_tensor
# 对预测框bbox进行解码x1y1x2y2,仍为相对于当前特征图大小的尺寸。
# pred_bboxes(bs, n_anchors, 4)
pred_bboxes = self._bbox_decode(anchor_points_s, pred_distri)
gt_labels = gt_meta['gt_class']
gt_bboxes = gt_meta['gt_bbox']
pad_gt_mask = gt_meta['pad_gt_mask']
# ========================正负样本分配======================
# assigned_labels(bs, n_anchors) 对于每张图片来说,n_anchors中的每一个anchor匹配到的gt的类别标签。
# assigned_bboxes(bs, n_anchors, 4) 对于每张图片来说,n_anchors中的每一个anchor匹配到的gt的坐标标签。
# assigned_scores(bs, n_anchors, num_classes) 对于每张图片来说,n_anchors中的每一个anchor匹配到的gt的score标签。
# 正负样本分配ATSS
if gt_meta['epoch_id'] < self.static_assigner_epoch:
assigned_labels, assigned_bboxes, assigned_scores = \
self.static_assigner(
anchors,
num_anchors_list,
gt_labels,
gt_bboxes,
pad_gt_mask,
bg_index=self.num_classes,
pred_bboxes=pred_bboxes.detach() * stride_tensor)
alpha_l = 0.25
# 正负样本分配TAL
else:
assigned_labels, assigned_bboxes, assigned_scores = \
self.assigner(
pred_scores.detach(),
pred_bboxes.detach() * stride_tensor,
anchor_points,
gt_labels,
gt_bboxes,
pad_gt_mask,
bg_index=self.num_classes)
alpha_l = -1
# 对目标框target进行解码decode成每个特征层尺度的非归一化大小(除以了stride),框格式xyxy
assigned_bboxes /= stride_tensor
# 分类损失cls loss
if self.use_varifocal_loss:
# ????????这块为什么要加1
one_hot_label = F.one_hot(assigned_labels, self.num_classes+1)[..., :-1]
loss_cls = self._varifocal_loss(pred_scores, assigned_scores, one_hot_label)
else:
loss_cls = self._focal_loss(pred_scores, assigned_scores, alpha_l)
assigned_scores_sum = assigned_scores.sum()
if paddle.distributed.get_world_size() > 1:
paddle.distributed.all_reduce(assigned_scores_sum)
assigned_scores_sum = paddle.clip(assigned_scores_sum / paddle.distributed.get_world_size(), min=1)
loss_cls /= assigned_scores_sum
# 回归损失bbox loss
loss_l1, loss_iou, loss_dfl = \
self._bbox_loss(pred_distri, pred_bboxes, anchor_points_s, assigned_labels,
assigned_bboxes, assigned_scores, assigned_scores_sum)
# 总的损失loss
loss = self.loss_weight['class'] * loss_cls + self.loss_weight['iou'] * loss_iou + self.loss_weight['dfl'] * loss_dfl
return {'loss': loss}
def post_process(self, head_outs, img_shape, scale_factor):
pred_scores, pred_dist, anchor_points, stride_tensor = head_outs
pred_bboxes = batch_distance2bbox(anchor_points,
pred_dist.transpose([0, 2, 1]))
pred_bboxes *= stride_tensor
# scale bbox to origin
scale_y, scale_x = paddle.split(scale_factor, 2, axis=-1)
scale_factor = paddle.concat(
[scale_x, scale_y, scale_x, scale_y], axis=-1).reshape([-1, 1, 4])
pred_bboxes /= scale_factor
if self.exclude_nms:
# `exclude_nms=True` just use in benchmark
return pred_bboxes.sum(), pred_scores.sum()
else:
bbox_pred, bbox_num, _ = self.nms(pred_bboxes, pred_scores)
return bbox_pred, bbox_num
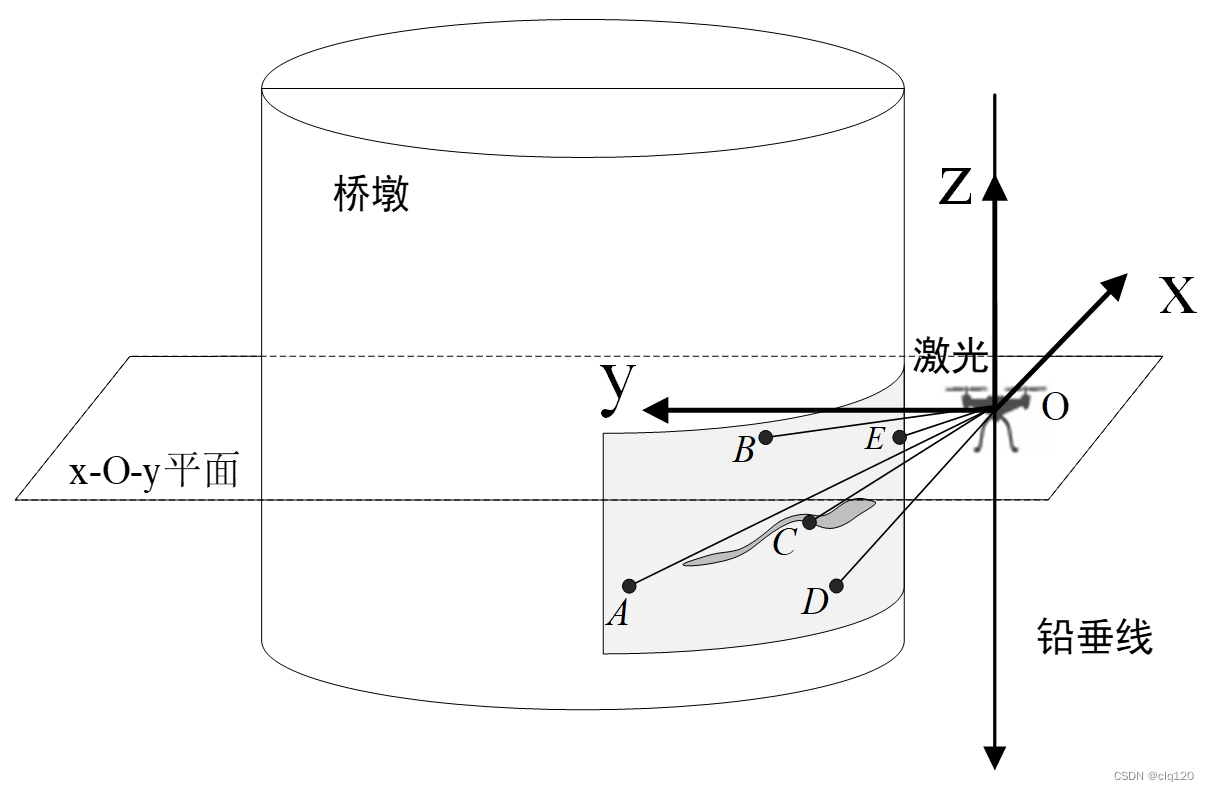
2、桥梁曲面处损伤的实际比例换算
针对乡村道路桥梁大多为梁式、拱式的特点,现有的仪器设备不能很好的检测乡村道路桥梁的损伤。而直接使用图像处理技术进行曲面处的损伤评估,一般存在较大的偏角误差。因此,我们针对乡村道路桥梁曲面处损伤检测的问题,建立数学模型,将曲面损伤图像转换为二维平面图像。
我们使用5个激光传感器组成“N”型激光阵列,获取桥梁曲面损伤处与无人机之间的距离;然后,通过分析多尺寸圆柱投影的共性特征,建立桥梁曲面处的数学模型,使用获取的距离信息计算曲面处的曲率半径;最后建立曲线投影数学模型,采用微元法来解决曲线与直线映射关系的坐标换算,获取真实损伤图像。经过重庆亚派桥梁工程质量检测有限公司的检测,我们的曲面损伤测量误差在5%以内,完全超过大多数损伤检测仪器的检测效果。
3、一桥双报告
无人机搭载的AI处理器应用模糊数学中的模糊综合评估方法,通过建模、分级,确定各级因素域及权重,得出各级评价向量,给定桥梁整体结构损伤度。最后根据最大隶属原则和非对称贴近度法等方法评估出桥梁损伤等级。最后分析损伤原因,并借助智能化决策系统的相关先进理念和方法,通过对养护决策环节中各要素之间的关系梳理,结合具体的判决阈值的设置,进行分步判断,并为所需养护的具体病害设置相匹配的养护预案。
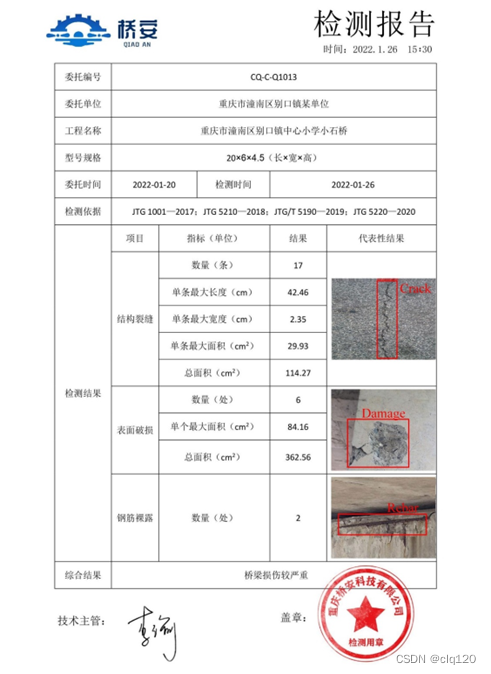
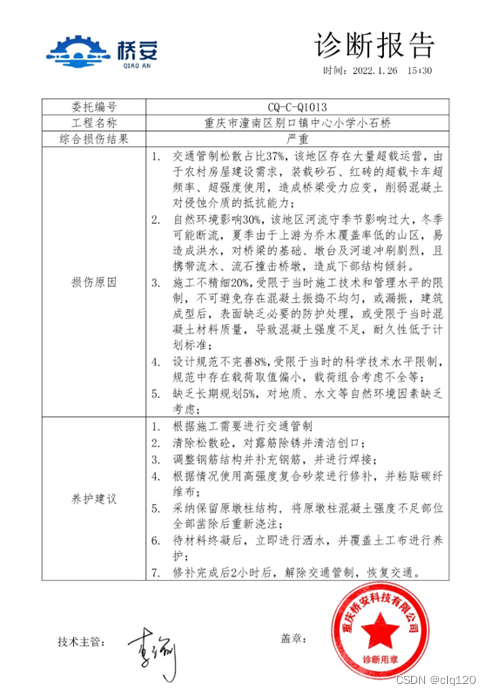
4、安全检测云平台
为了长期有效存储检测数据,本团队设计开发了乡村道路桥梁安全检测云平台,该云平台数据库包括各地区的桥梁检测数量、损伤类别、损伤情况占比等数据,将数据进行可视化处理,直观地显示桥梁损伤状态、发展趋势及养护情况。该云平台支持多终端实时显示,同时为各地区的道路桥梁管理部门免费开放登录权限,随时查看检测数据,极大地方便了政府相关部门对乡村道路桥梁的安全监测。


此文章为搬运
原项目链接
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1436条内容
已为社区贡献1436条内容









所有评论(0)