基于LightGBM实现银行客户信用违约预测
对数据进行EDA,其中NaN的填充,再次对离散和数值型的进行分类,并对离散的批量Encode,最后使用LightGBM建模并训练,预测违约风险。
★★★ 本文源自AlStudio社区精品项目,【点击此处】查看更多精品内容 >>>
题目地址:Coggle竞赛
1.赛题介绍
信用评分卡(金融风控)是金融行业和通讯行业常见的风控手段,通过对客户提交的个人信息和数据来预测未来违约的可能性。对客户进行信用评分是一个常见的分类问题。
在本次赛题中需要参赛选手建立机器学习模型来预测申请人是“好”还是“坏”客户,与其他任务不同,没有给出“好”或“坏”的定义。 您应该使用一些技术,例如年份分析来构建您的标签。
2.数据介绍
赛题包含两部分训练集和测试集,选手需要在训练集上进行搭建模型,然后在测试集进行预测。
- train.csv,训练集
- test.csv,测试集
- sample_submission.csv,测试集提交样例
数据字段介绍如下:
- ID,客户唯一标识
- Gender,客户性别
- Age,客户年龄
- Region_Code,地区代码
- Occupation,客户职业
- Channel_Code,客户渠道代码
- Vintage,客户服务月份
- Credit_Product,信贷产品类型
- AvgAccountBalance,客户最近12个月平均账户余额
- Is_Active,客户最近3个月是否活跃
3.提交格式
评分使用准确率进行评分,准确率值越大越好。
- 实操方案不允许使用外部数据集,不允许使用任何外部预训练模型。
- 实操方案需要在指定平台进行评分,提交csv格式。
提交格式样例:
ID,Target
AXM2EH3R,1
8ETNJAUW,1
VCSJTEPW,0
9EOYOOHV,0
4.总体思路
- 对缺失值进行处理,原本想全删掉,结果test也有,就填充了;
- 对离散值处理,直接分类,离散数据Encoder;
- 数据EDA,主要是确定各特征分布,其中离散的太多,时间太久就取消了;
- 使用lightGBM建立模型并训练;
- 保存结果并提交。
学习自:
- 江某1111号机数据Encode方式,非常方便。
- 江某1111号机 基于LightGBM实现银行客户认购产品预测
二、数据载入
1.数据读取
通过pandas读取数据
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df=pd.read_csv("data/data207852/train.csv")
test=pd.read_csv("data/data207852/test.csv")
test.head(10)
| ID | Gender | Age | Region_Code | Occupation | Channel_Code | Vintage | Credit_Product | Avg_Account_Balance | Is_Active | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | AXM2EH3R | Female | 43 | RG284 | Self_Employed | X3 | 26 | Yes | 1325325 | Yes |
| 1 | 8ETNJAUW | Female | 46 | RG282 | Self_Employed | X2 | 14 | No | 634489 | No |
| 2 | VCSJTEPW | Female | 28 | RG254 | Self_Employed | X1 | 15 | No | 2215655 | No |
| 3 | 9EOYOOHV | Male | 58 | RG265 | Other | X3 | 15 | Yes | 925929 | Yes |
| 4 | S4B53OKJ | Male | 75 | RG260 | Other | X3 | 111 | No | 721825 | Yes |
| 5 | 3DTSVD9Y | Female | 51 | RG268 | Self_Employed | X1 | 57 | No | 490345 | No |
| 6 | 8WYWQUUX | Male | 32 | RG279 | Salaried | X1 | 33 | No | 650483 | No |
| 7 | FPQTNHGY | Female | 38 | RG270 | Salaried | X1 | 33 | NaN | 369777 | No |
| 8 | UXCKDQ34 | Male | 56 | RG254 | Self_Employed | X2 | 62 | Yes | 2406880 | Yes |
| 9 | CFTGOZHH | Female | 29 | RG283 | Salaried | X1 | 20 | No | 659053 | No |
df.head(10)
| ID | Gender | Age | Region_Code | Occupation | Channel_Code | Vintage | Credit_Product | Avg_Account_Balance | Is_Active | Target | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | ZYFGCP3R | Male | 58 | RG264 | Self_Employed | X2 | 19 | No | 552449 | Yes | 0 |
| 1 | MQJBCRCF | Female | 45 | RG271 | Self_Employed | X3 | 104 | Yes | 525206 | No | 1 |
| 2 | UZOQRG46 | Female | 30 | RG278 | Other | X1 | 25 | No | 724718 | No | 0 |
| 3 | GCX6RVZS | Female | 52 | RG283 | Self_Employed | X1 | 43 | Yes | 1452453 | No | 0 |
| 4 | 9V6BRARI | Female | 76 | RG254 | Other | X1 | 57 | No | 1895762 | No | 0 |
| 5 | WUGN99OM | Male | 28 | RG275 | Salaried | X1 | 33 | No | 885576 | No | 0 |
| 6 | EQ4CBNED | Male | 31 | RG268 | Salaried | X1 | 33 | No | 653135 | Yes | 0 |
| 7 | JZZ7MPIR | Male | 48 | RG259 | Entrepreneur | X2 | 67 | Yes | 389553 | Yes | 1 |
| 8 | KVHMRSES | Female | 31 | RG254 | Salaried | X1 | 33 | No | 1543001 | No | 0 |
| 9 | KS45GJCT | Female | 48 | RG273 | Other | X3 | 105 | NaN | 360005 | Yes | 1 |
df.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 195725 entries, 0 to 195724
Data columns (total 11 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 ID 195725 non-null object
1 Gender 195725 non-null object
2 Age 195725 non-null int64
3 Region_Code 195725 non-null object
4 Occupation 195725 non-null object
5 Channel_Code 195725 non-null object
6 Vintage 195725 non-null int64
7 Credit_Product 172279 non-null object
8 Avg_Account_Balance 195725 non-null int64
9 Is_Active 195725 non-null object
10 Target 195725 non-null int64
dtypes: int64(4), object(7)
memory usage: 16.4+ MB
2.NaN处理
发现Credit_Product列有空值,怎么办?仔细一看test也有空值,不能简单的删除了,那就看这个值哪个多就填写哪个了。
# 统计某列值
df['Credit_Product'].unique()
array(['No', 'Yes', nan], dtype=object)
# 统计某列出现某值的次数
df['Credit_Product'].value_counts()
No 114910
Yes 57369
Name: Credit_Product, dtype: int64
可以看出,该列值主要为No,因此缺失值nan设置为No。
test.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 50000 entries, 0 to 49999
Data columns (total 10 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 ID 50000 non-null object
1 Gender 50000 non-null object
2 Age 50000 non-null int64
3 Region_Code 50000 non-null object
4 Occupation 50000 non-null object
5 Channel_Code 50000 non-null object
6 Vintage 50000 non-null int64
7 Credit_Product 44121 non-null object
8 Avg_Account_Balance 50000 non-null int64
9 Is_Active 50000 non-null object
dtypes: int64(3), object(7)
memory usage: 3.8+ MB
# 空值填No
df=df.fillna('No')
test=test.fillna('No')
2.数据EDA
-
duration分箱展示
-
查看数据分布
-
数据相关图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
%matplotlib inline
# 按年龄分布查看
ages=[22,30,40,50,60,70,80,90]
df1=df[df['Credit_Product']=='Yes']
binning=pd.cut(df1['Age'],ages,right=False)
time=pd.value_counts(binning)
# 可视化
time=time.sort_index()
fig=plt.figure(figsize=(6,2),dpi=120)
sns.barplot(time.index,time,color='royalblue')
x=np.arange(len(time))
y=time.values
for x_loc,jobs in zip(x,y):
plt.text(x_loc, jobs+2, '{:.1f}%'.format(jobs/sum(time)*100), ha='center', va= 'bottom',fontsize=8)
plt.xticks(fontsize=8)
plt.yticks([])
plt.ylabel('')
plt.title('duration_yes',size=8)
sns.despine(left=True)
plt.show()

# 分离数值变量与分类变量
Nu_feature = list(df.select_dtypes(exclude=['object']).columns)
Ca_feature = list(df.select_dtypes(include=['object']).columns)
#查看训练集与测试集数值变量分布
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
plt.figure(figsize=(15,5))
Nu_feature.remove('Target')
# 根据数值型分布查看
i=1
for col in Nu_feature:
ax=plt.subplot(1,3,i)
ax=sns.kdeplot(df[col],color='red')
ax=sns.kdeplot(test[col],color='cyan')
ax.set_xlabel(col)
ax.set_ylabel('Frequency')
ax=ax.legend(['train','test'])
i+=1
plt.show()

查看离散变量分布
由于时间太久,故不测
col1=Ca_feature
plt.figure(figsize=(20,10))
j=1
for col in col1:
ax=plt.subplot(6,3,j)
ax=plt.scatter(x=range(len(df)),y=df[col],color='red')
plt.title(col)
j+=1
k=7
for col in col1:
ax=plt.subplot(6,3,k)
ax=plt.scatter(x=range(len(test)),y=test[col],color='cyan')
plt.title(col)
k+=1
plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.4,hspace=0.3)
plt.show()
# 离散数据Encoder
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
lb = LabelEncoder()
cols = Ca_feature
for m in cols:
df[m] = lb.fit_transform(df[m])
test[m] = lb.fit_transform(test[m])
correlation_matrix=df.corr()
plt.figure(figsize=(12,10))
# 热力图
sns.heatmap(correlation_matrix,vmax=0.9,linewidths=0.05,cmap="RdGy")
<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot at 0x7fa254ac6150>

三、建立模型
1. 切割训练集和测试集
这里使用留出法划分数据集,将数据集分为自变量和因变量。
按比例切割训练集和测试集(一般测试集的比例有30%、25%、20%、15%和10%),使用分层抽样,设置随机种子以便结果能复现
from lightgbm.sklearn import LGBMClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, auc, roc_auc_score
X=df.drop(columns=['ID','Target'])
Y=df['Target']
test=test.drop(columns='ID')
# 划分训练及测试集
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split( X, Y,test_size=0.3,random_state=1)
2. 模型创建
创建基于树的分类模型(lightgbm)
这些模型进行训练,分别的到训练集和测试集的得分
# 建立模型
gbm = LGBMClassifier(n_estimators=600,learning_rate=0.01,boosting_type= 'gbdt',
objective = 'binary',
max_depth = -1,
random_state=2022,
metric='auc')
四、模型训练
交叉验证介绍
- 交叉验证(cross-validation)是一种评估泛化性能的统计学方法,它比单次划分训练集和测试集的方法更加稳定、全面。
- 在交叉验证中,数据被多次划分,并且需要训练多个模型。
- 最常用的交叉验证是 k 折交叉验证(k-fold cross-validation),其中 k 是由用户指定的数字,通常取 5 或 10。
1.模型训练
# 交叉验证
result1 = []
mean_score1 = 0
n_folds=5
kf = KFold(n_splits=n_folds ,shuffle=True,random_state=2022)
for train_index, test_index in kf.split(X):
x_train = X.iloc[train_index]
y_train = Y.iloc[train_index]
x_test = X.iloc[test_index]
y_test = Y.iloc[test_index]
gbm.fit(x_train,y_train)
y_pred1=gbm.predict_proba((x_test),num_iteration=gbm.best_iteration_)[:,1]
print('验证集AUC:{}'.format(roc_auc_score(y_test,y_pred1)))
mean_score1 += roc_auc_score(y_test,y_pred1)/ n_folds
y_pred_final1 = gbm.predict_proba((test),num_iteration=gbm.best_iteration_)[:,1]
y_pred_test1=y_pred_final1
result1.append(y_pred_test1)
验证集AUC:0.7889931707362382
验证集AUC:0.7894677985120346
验证集AUC:0.7931272562656144
验证集AUC:0.7850546301430752
验证集AUC:0.7876841341097264
2.模型评估
# 模型评估
print('mean 验证集auc:{}'.format(mean_score1))
cat_pre1=sum(result1)/n_folds
mean 验证集auc:0.7888653979533378
3.输出结果
将预测结果按照指定格式输出到result.csv文件中
ret1=pd.DataFrame(cat_pre1,columns=['Target'])
ret1['Target']=np.where(ret1['Target']>0.5,'1','0').astype('str')
result = pd.DataFrame()
test=pd.read_csv("data/data207852/test.csv")
result['ID'] = test['ID']
result['Target'] = ret1['Target']
result.to_csv('result.csv',index=False)
print(test.columns)
Index(['ID', 'Gender', 'Age', 'Region_Code', 'Occupation', 'Channel_Code',
'Vintage', 'Credit_Product', 'Avg_Account_Balance', 'Is_Active'],
dtype='object')
', ‘Is_Active’],
dtype=‘object’)
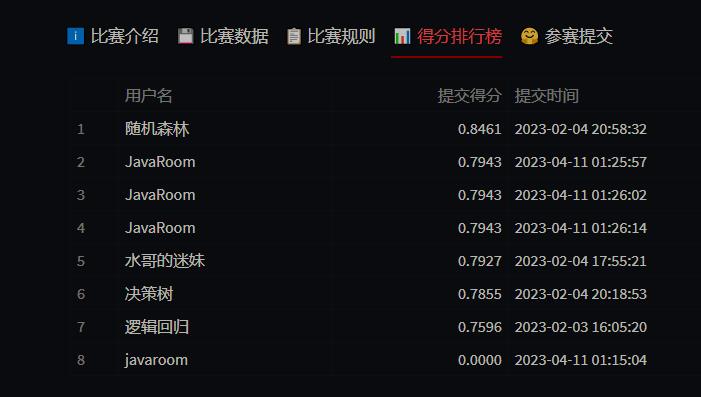
五、提交
第一次提交错了,第二次刷新过头了

此文章为搬运
原项目链接
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1438条内容
已为社区贡献1438条内容








所有评论(0)